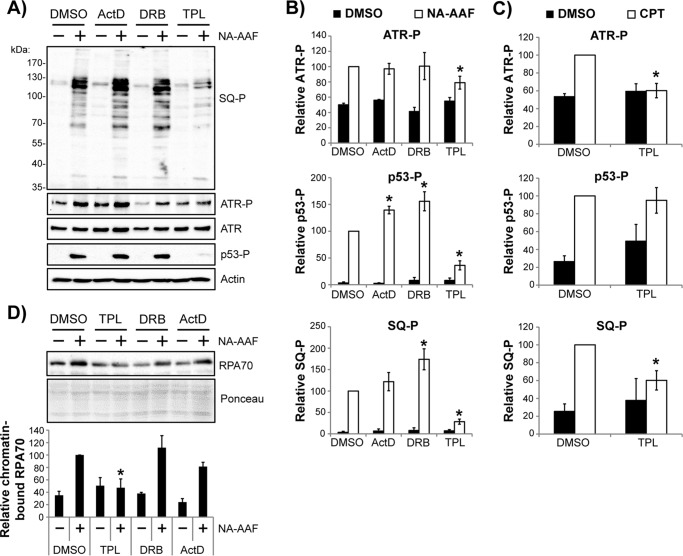
Figure 6.
Inhibition TFIIH with triptolide abrogates the bulk of ATR kinase signaling in response to DNA damage in non-cycling cells. A, non-cycling HaCaT cells were pretreated with DMSO or the indicated transcription inhibitor for 30 min prior to exposure to 20 μm NA-AAF. Cells were harvested 2 h later and analyzed by immunoblotting. B, quantitation of ATR, p53, and ATM/ATR substrate (SQ-P) phosphorylation from four independent experiments performed as in A. The phosphoprotein samples from cells treated with DMSO + NA-AAF were set to an arbitrary value of 100, and all other samples were compared with this value. C, non-cycling HaCaT cells were treated and analyzed as in A and B, except that cells were treated with camptothecin instead of NA-AAF. *, p < 0.05l; indicating a significant difference in protein phosphorylation between drug-treated and DMSO-treated cells. D, cells were treated as in A, except that cells were harvested 1 h after NA-AAF administration and then fractionated to isolate chromatin-associated proteins. The graph shows the relative level of chromatin-associated RPA70 (normalized to Ponceau staining) from three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; indicating a significant difference in RPA chromatin level between TPL- and DMSO-treated cells.