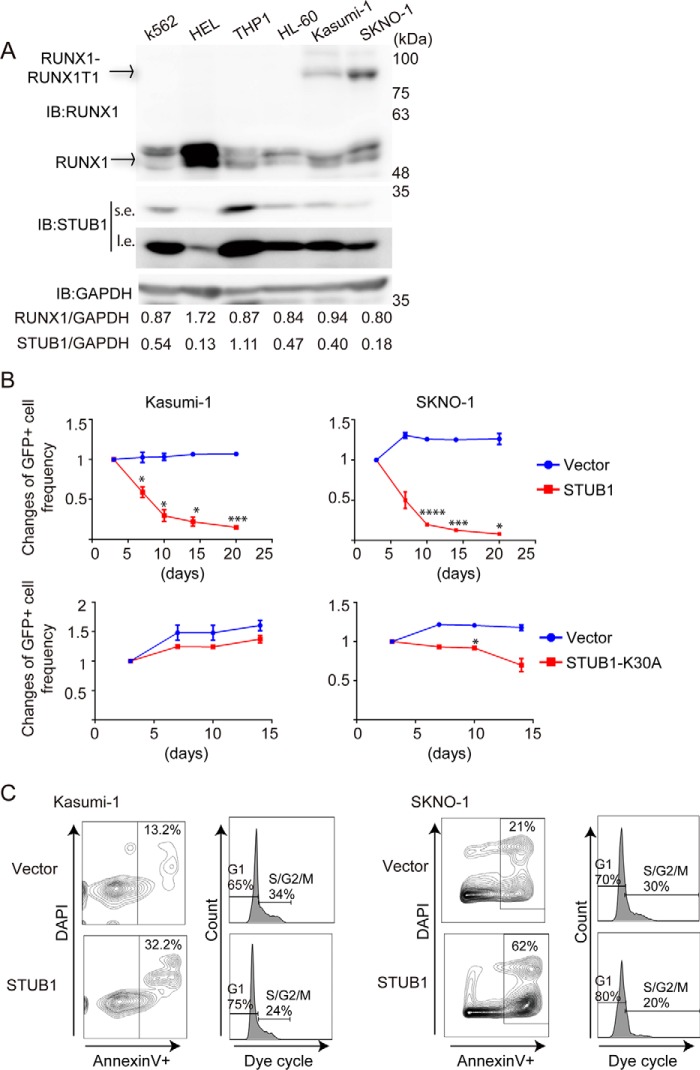
Figure 9.
STUB1 induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of RUNX1–RUNX1T1 leukemia cells. A, STUB1 and RUNX1 were expressed in myeloid leukemia cell lines. RUNX1–RUNX1T1 leukemia cells (Kasumi-1 and SKNO-1) showed relatively low levels of STUB1 expression. Note that HEL cells showed the highest and the lowest expression of RUNX1 and STUB1, respectively. B, a vector control, wild-type STUB1, or STUB1-K30A (coexpressing GFP) was transduced into Kasumi-1 and SKNO-1 cells. The mixed transduction culture containing both transduced GFP+ and nontransduced GFP− cells were passaged to score the frequency of the GFP+ cell by flow cytometric analysis as a measure of the impact of the transduced gene on cellular proliferation rate. The initial frequency of GFP+ cells immediately after transduction was set as 1. Two independent experiments were performed, and data are shown as mean ± S.E. (*, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.005; ****, p < 0.001). Overexpression of STUB1, but not STUB1-K30A, showed a strong growth-inhibitory effect in these cells. C, Kasumi-1 and SKNO-1 cells were transduced with a vector or STUB1 (coexpressing GFP), and GFP+ cells were sorted. Cell-cycle status and apoptosis were assessed in these GFP+ cells. STUB1 overexpression resulted in the increased or decreased frequency of Annexin V+ or S/G2/M phase cells, respectively. IB, immunoblot.