Figure 7.
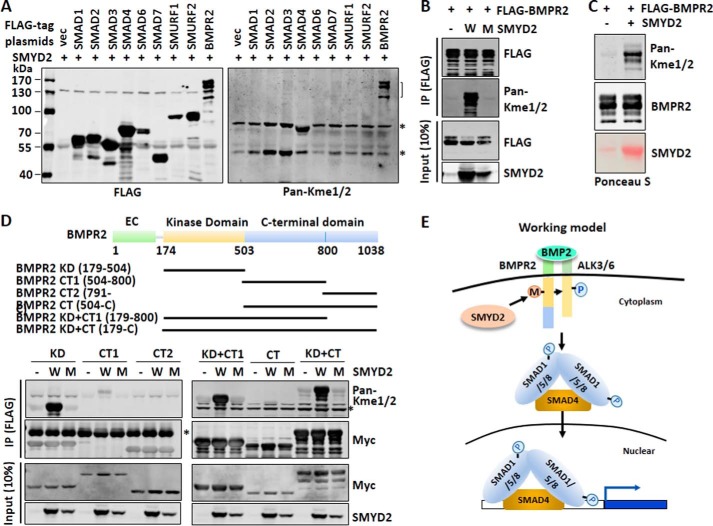
SMYD2 methylates BMPR2 at its kinase domain. A, Western blot analysis using a pan-mono/di-methylated lysine antibody revealed specific methylation of BMPR2 by SMYD2. 293T cells were co-transfected with SMYD2 and FLAG-SMADs, SMURFs, or BMPR2 for 48 h. Various FLAG-tagged proteins were immunoprecipitated from the whole-cell extracts with anti-FLAG antibody, and methylation was detected by Western blot analysis using a pan-mono/di-methylated lysine antibody (Pan-Kme1/2). The methylated BMPR2 is indicated by a bracket. Asterisks indicate two nonspecific bands, which were likely Hsp70, an abundant chaperone protein often heavily methylated endogenously, and IgG heavy chain. B, methylation of BMPR2 by SMYD2 required SMYD2 catalytic activity. 293T cells were co-transfected with FLAG-BMPR2 and either wild-type SMYD2 (W) or SMYD2 Y240A mutant (M) for 48 h. The subsequent immunoprecipitation (IP)-Western blot analysis was as above. C, SMYD2 methylated BMPR2 in vitro. FLAG-BMPR2 was expressed in 293T cells via transient transfection and purified by anti-FLAG antibody. The immunoaffinity-purified BMPR2 was subjected to in vitro methylation reactions using bacterially expressed and purified His6-SMYD2 (SMYD2). The methylation of FLAG-BMPR2 was detected by Western blot analysis using Pan-Kme1/2. D, SMYD2 methylates the BMPR2 kinase domain in vivo. The upper panel shows various truncated BMPR2 constructs. Various Myc-tagged SMYD2 constructs were co-transfected with the wild-type (W) or SMYD2-Y240A mutant (M) for 48 h, followed by immunoprecipitation with anti-Myc antibody and Western blot analysis with Pan-Kme1/2 and other indicated antibodies. E, working model illustrating how SMYD2 may potentiate BMP signaling transduction by methylating BMPR2. SMYD2 interacts with and methylates BMPR2 within its kinase domain (KD). This methylation may promote the BMPR2 kinase activity and therefore phosphorylation of the type 1 receptor. The activated type 1 receptor then phosphorylates SMAD1/5 and promotes SMAD1/5 nuclear entry and interaction with SMAD4, and consequently it promotes BMP-induced target gene expression.