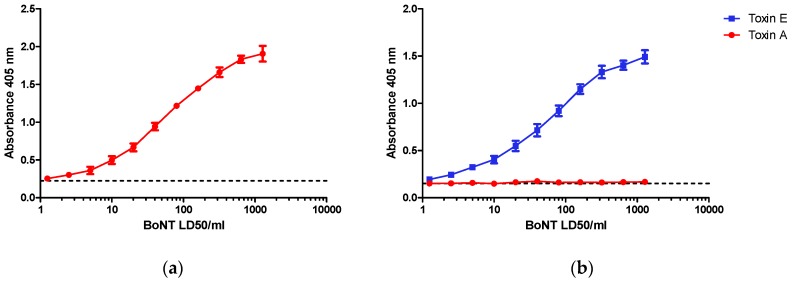
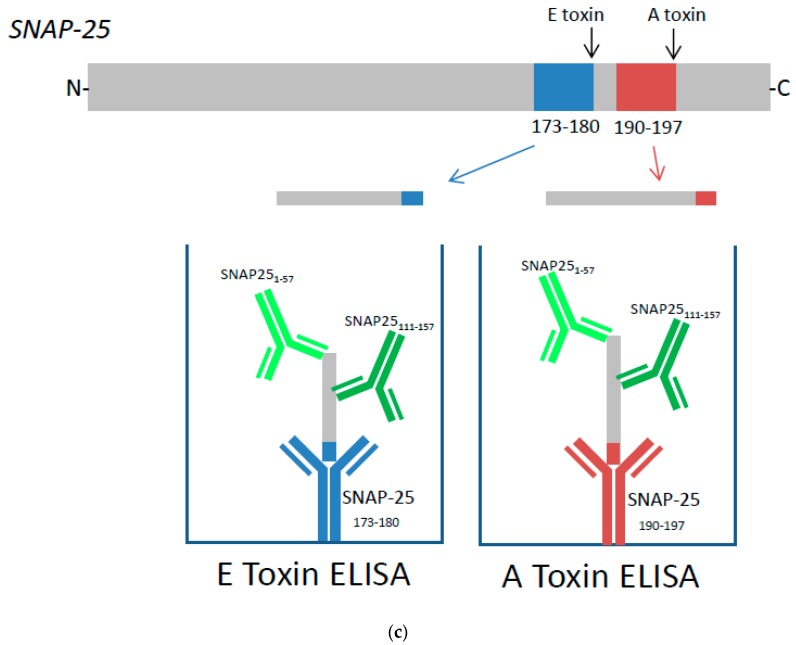
Figure 2.
Dose dependent detection of cleaved SNAP-25 specific for (a) Botulinum toxins (BoNT)/A and (b) BoNT/E toxins. SiMa cells were differentiated for 3 days on 96-well tissue culture plates and treated with either purified BoNT/A or BoNT/E toxins in a range of concentrations between 1–1280 LD50/mL (~5 pg/mL to ~5 ng/mL). After 48 h exposure, cells were lysed and subjected to toxin specific capture ELISA for detection of either BoNT/A (a) or BoNT/E (b) cleaved SNAP-25. Dotted line indicates controls where cells were not exposed to toxins. Results are from one typical assay performed on at least three independent occasions and each data set is a mean from four individual wells ±SD. (c) Schematic overview of capture ELISA for BoNT/A and BoNT/E: BoNT/A cleaves SNAP-25 between amino acids 197 and 198 and the cleavage product is captured using a specific neo-epitope antibody raised against a peptide corresponding to amino acids 190–197 of SNAP-25 (SNAP-25190–197). BoNT/E cleaves SNAP-25 between amino acids 180 and 181 and the cleavage product is captured using a specific neo-epitope antibody raised against a peptide corresponding to amino acids 173–180 of SNAP-25 (SNAP-25173–180). The captured cleavage product is then detected using two polyclonal detection antibodies that bind to two distinct sites, SNAP-251–57 and SNAP-25111–157.