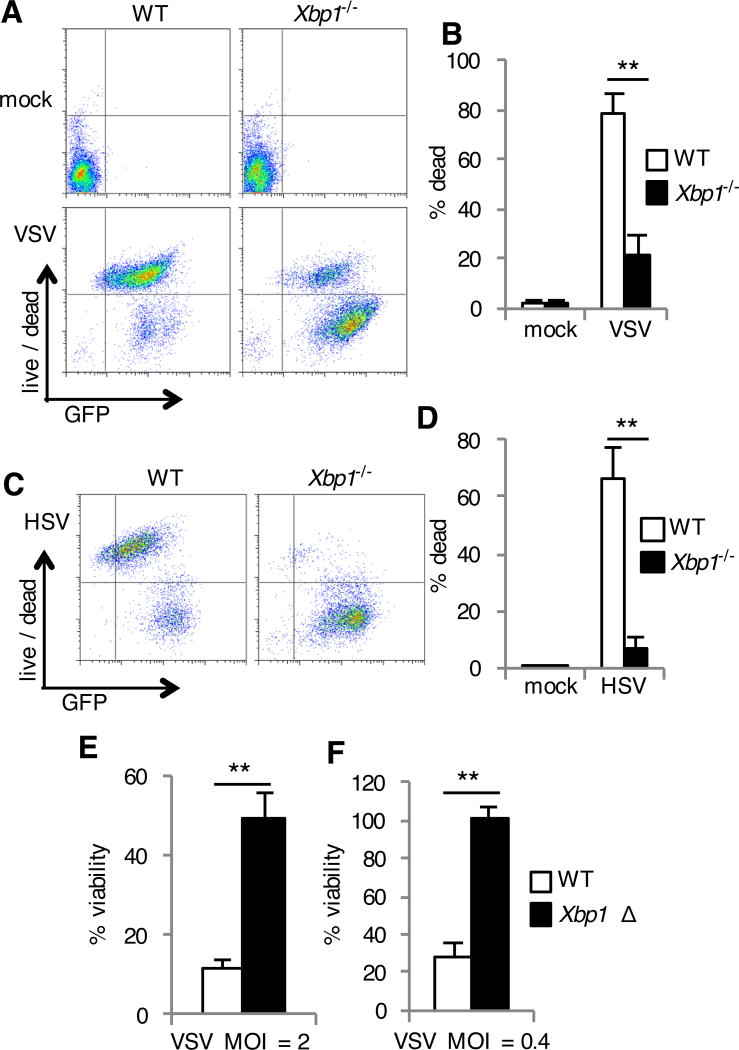
Fig. 2. Xbp1-deficient cells are resistant to cell death during infection with VSV and HSV.
(A to D) WT and Xbp1−/− MEFs were left uninfected (mock) or were infected with VSV-GFP (A and B) or HSV-1-GFP (C and D) for 24 hours. Cell death was then assessed with a membrane-impermeant, amine-reactive fluorescent dye, which was measured by flow cytometry. Data are from one experiment representative of three experiments (A and C). The percentages of dead cells were then determined. Data are means ± SD from three independent experiments (B and D). (E and F) BMDMs were cultured from Xbp1flox/flox ESR Cre+ (Xbp1 Δ), or Cre- littermate (WT) mice in the presence of tamoxifen. Cells were infected with VSV-GFP at the indicated multiplicity of infection (MOI) for 24 hours. Viability was then assessed by measuring MTS reduction. Data are means ± SD of three replicates and are representative of three experiments (E and F).**P < 0.01 compared to WT, unpaired t test.