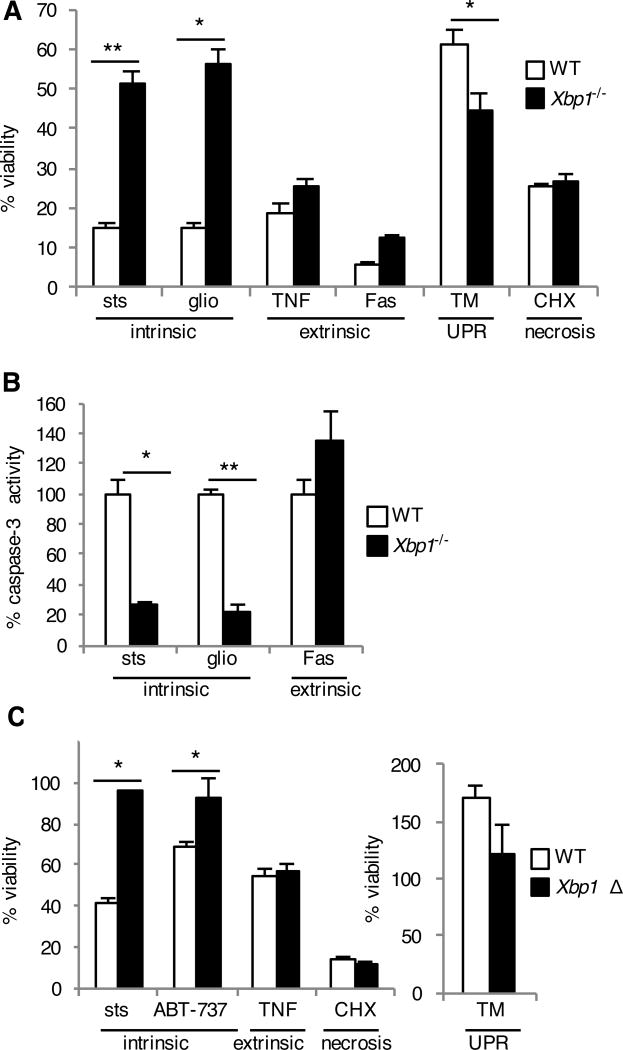
Fig. 4. Xbp1-deficient cells are resistant to the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis.
(A and B) WT and Xbp1−/− MEFs were treated with staurosporine (sts), gliotoxin (glio), tumor necrosis factor + low dose cycloheximide (TNF), Fas antibody + low dose cycloheximide (Fas), tunicamycin (TM) to induce the unfolded protein response (UPR) or high dose cycoheximide (CHX). Twenty-four hours later, viability was assessed by measuring MTS reduction (A). Seven hours after treatment, caspase-3 activity was assessed by measuring fluorometric substrate cleavage, and is shown relative to WT cells (B). Data are means ± SD of three replicates and are representative of three experiments. (C) BMDMs were cultured from Xbp1flox/flox ESR Cre+ (Xbp1 Δ), or Cre- littermate (WT) mice in the presence of tamoxifen and treated with cell death inducers as in (A). Twenty-four hours later, viability was assessed by measuring MTS reduction. Data are means ± SD of three replicates and are representative of three experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001 compared to WT, unpaired t test.