Figure 1.
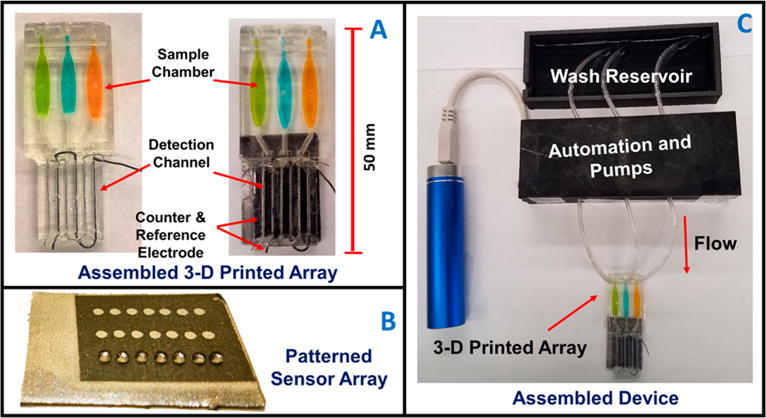
Automated genotoxicity screening array: (A) 3-D printed devices without (left) and with (right) microwell chip and counter electrode wires inserted showing the sample chambers containing dye solutions. (B) Microwell-patterned pyrolytic graphite detection array showing the first row holding 1 μL water droplets retained by the hydrophobic microwell boundaries. Each row is fed by a separate sample line. The working array features films of DNA, metabolic enzymes, and RuPVP in each microwell. (C) Assembled array system showing box enclosing electronic microprocessors and micropumps driven by a rechargeable battery and connected to the 3-D printed array below with a wash reservoir (top) containing pH 7.4 buffer.
