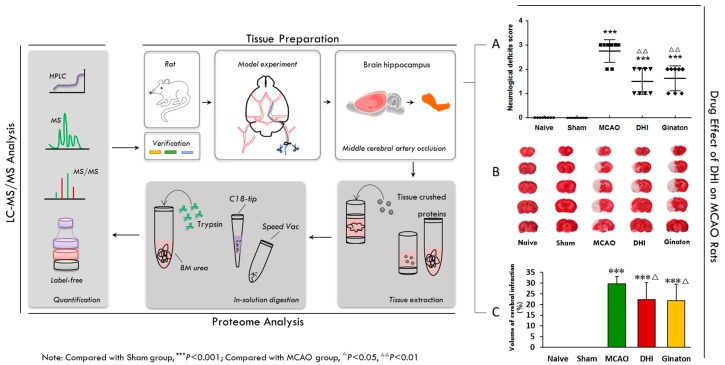
Figure 1.
Overview of the experimental workflow. Firstly, permanent occlusion of the middle cerebral artery (MCAO) was established in rats with an intraluminal silicon-coated filament (tissue preparation). Secondly, to ensure the reliability and rationality of the rat model of cerebral ischemic injury, an initial experiment revealed the success of the establishment of focal ischemic models (A,B,C). Thirdly, the hippocampal region of the model brains was tissue crushed and the protein extracted, after injury time of 24 h in focal ischemic models (tissue preparation). Fourthly, proteins for proteome analysis were tryptic digested in solution, desalted using a C18 pre-column, and subjected to LC and Q-Exactive analysis (proteome analysis). Finally, the peptide mixture was analyzed with online reverse-phase chromatography and mass spectrometry and a label-free approach was used for the quantitative analysis (LC-MS/MS Analysis). (A) The results of neurological deficits Score shown that DHI and Ginaton can improve neurological function in MCAO rats after 24 h ischaemic injury (Table 1, the date was tested by a rank sum test); (B,C) 2% TTC staining results and histogram shown that DHI and Ginaton can decrease the volume of cerebral infraction in MCAO rats. The results of TTC were tested by one way ANOVA and multiple testing (Table 2).