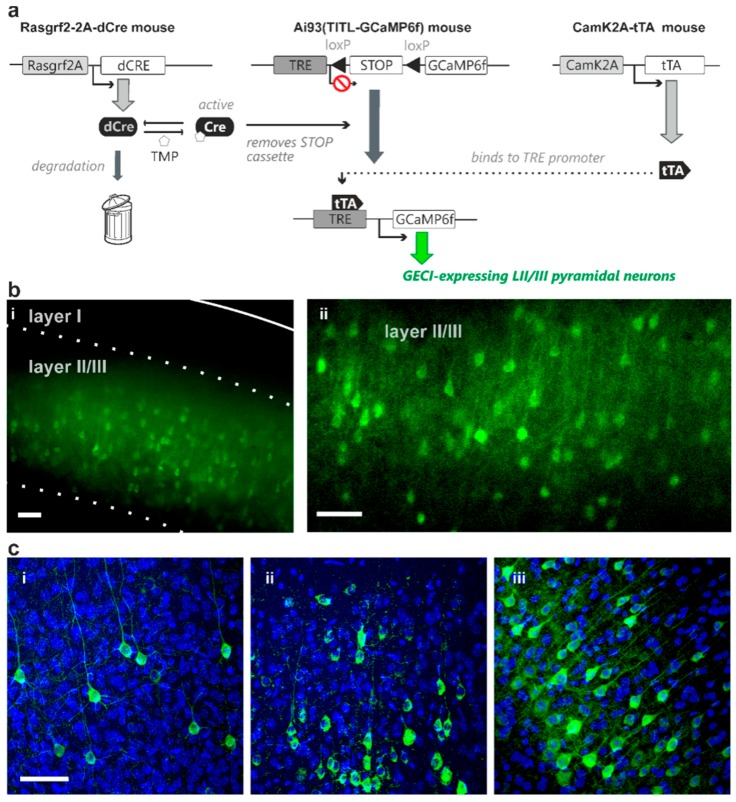
Figure 1.
Representative images of adjusted GECI expression probability of layer II/III pyramidal neurons achieved via dose-dependent TMP administration. (a) Transgenic strategy using the combination of both Cre-recombinase and transactivator intersectionally controls indicator expression in identified cell populations in Ai93 GCaMP6f indicator transgenic mice. The transgenic strategy shown here uses a destabilized form of Cre-recombinase driven by Rasgrf2-2A promoter (Rasgrf2-2A-dCre) that can be “de-destabilized” using TMP to remove the STOP cassette in layer II/III neurons. Transactivator expression driven by CaMK2A promoter (CaMK2A-tTA) in pyramidal neurons is also required for binding to the TRE promoter in the indicator mice for indicator expression (GCaMP6f in this transgenic diagram). This combination of dCre and tTA facilitates adjustable indicator expression probability of layer II/III pyramidal neurons by titratable TMP administration (b) GCaMP6f expression density remained high with total TMP dose administered at 50 mg/kg body weight (i; imaged using wide-field epifluorescence microscopy; solid line marks the pia, dashed line marks cortical layer boundaries) and 0.5 mg/kg body weight (ii; using confocal microscopy, single plane) (c) GCaMP6f expression with total TMP dose administered at 0.005 mg/kg body weight (i), 0.03 mg/kg body weight (ii), and 750 mg/kg body weight (iii) TMP concentrations resulted in different levels of GCaMP6f expression density (confocal microscopy). DAPI nuclei-counterstaining shows, in addition to pyramidal neurons, dense cell population including glia, GABAergic interneurons and blood vessel-related cells. Scale bar = 50 µm; stack thickness = 15 µm.