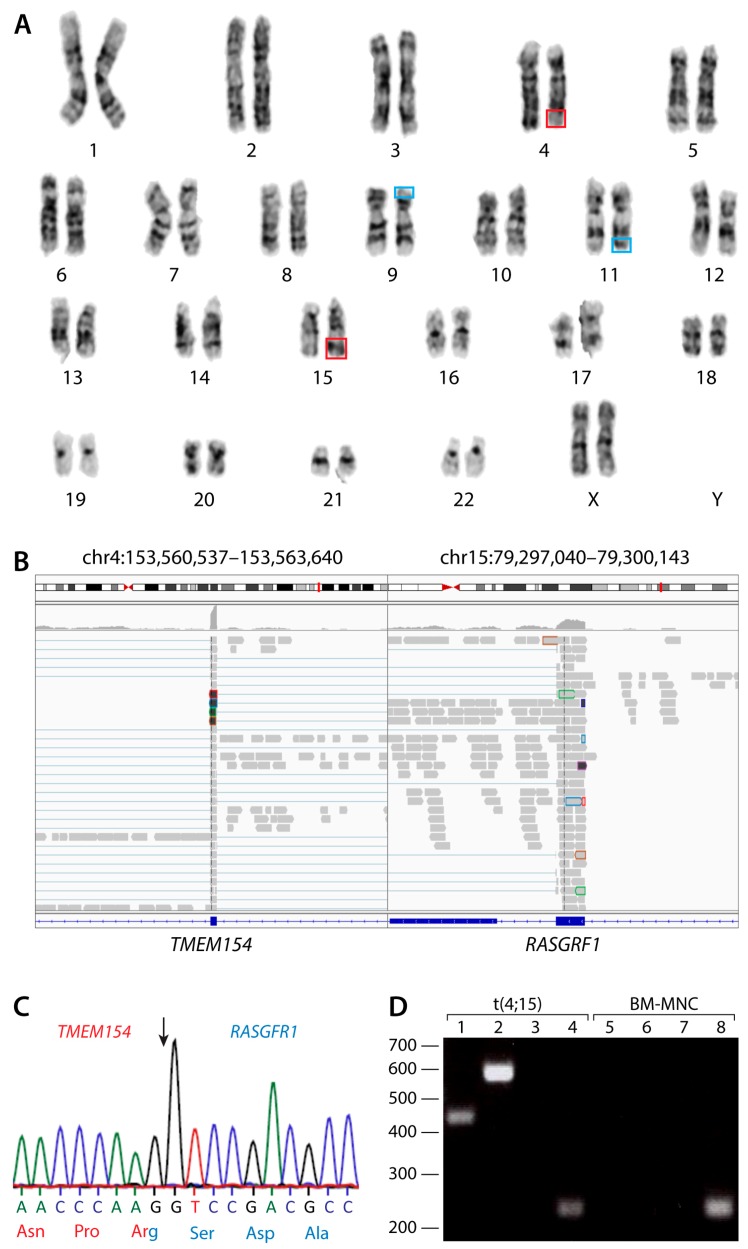
Figure 1.
Analysis of the t(4;15)(q31;q22) reciprocal chromosomal translocation. (A) Conventional karyotyping showing 46,XX,t(4;15)(q31;q22), outlined in red and t(9;11)(p22;q23), outlined in blue. Chromosome analysis was performed on 20 G-banded metaphase cells from multiple unstimulated cultures. Both translocations were present in all cells examined. (B) Breakpoint analysis of the novel fusion transcript produced by the t(4;15) chromosomal translocation. TMEM154 and RASGRF1 form a chimeric mRNA transcript with the breakpoint indicated by the black arrow. (C) Sanger sequencing chromatogram showing the transcribed sequence surrounding the breakpoint. (D) PCR analysis of and TMEM154-RASGRF1, RASGRF1-TMEM154, and TMEM154 transcripts. PCR was performed on t(4;15) acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells (lanes 1–4) and bone marrow mononuclear cells (BM-MNCs) from a healthy donor (lanes 5–8). Bands correspond to a 445 bp product amplified fromTMEM154-RASGRF1 mRNA (lanes 1 and 5), a 589 bp product amplified from TMEM154-RASGRF1 mRNA (lanes 2 and 6), and a 445 bp product amplified fromTMEM154 mRNA (lanes 4 and 8). No product was amplified using primers corresponding to RASGRF1-TMEM154 mRNA (lanes 3 and 7).