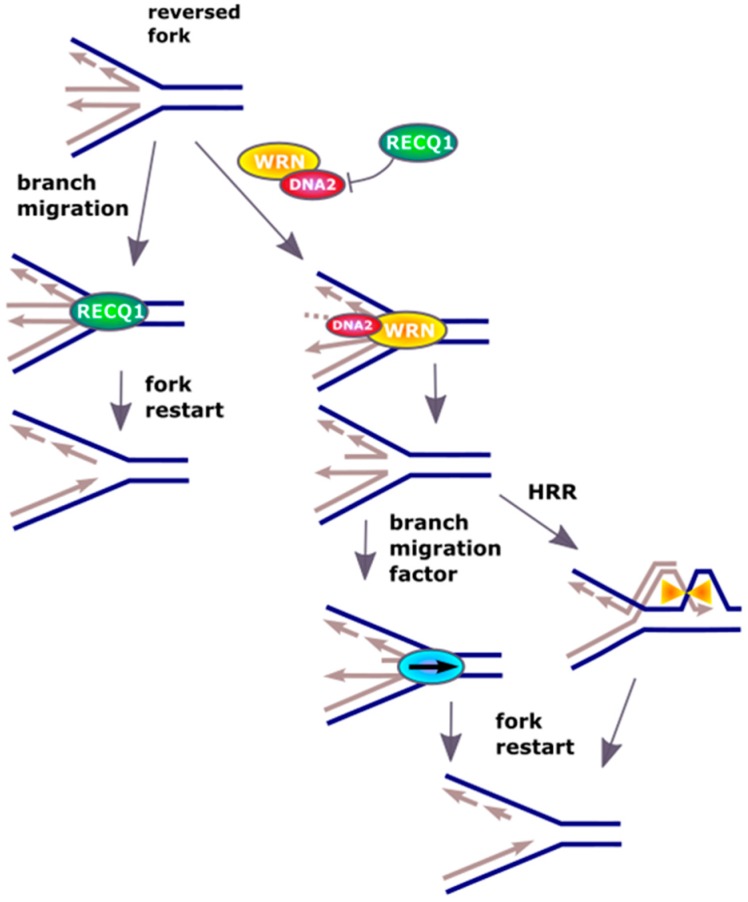
Figure 3.
DNA2 restarts reversed replication fork. Excessive unwinding of the template in DNA replication, resulting from escape of DNA helicase from DNA polymerase or DNA damage in the template, leads to regression of replication fork by pairing of the newly synthesized strands. Resulted “chicken foot” structure is primarily resolved by the RECQ1 helicase, but if its activity is inhibited or in RECQ1-deficient cells, DNA2 can cleave the single-strand 5′ end of the regressed fork assisted by ATP-ase activity of WRN (Werner syndrome ATP-dependent helicase) or BLM (Bloom syndrome protein) (not presented). The restart is preceded by the action of branch migration factors, not displayed in that scheme. Recombination mechanisms based on homology (HRR) are an alternative for RECQ1 and DNA2 action.