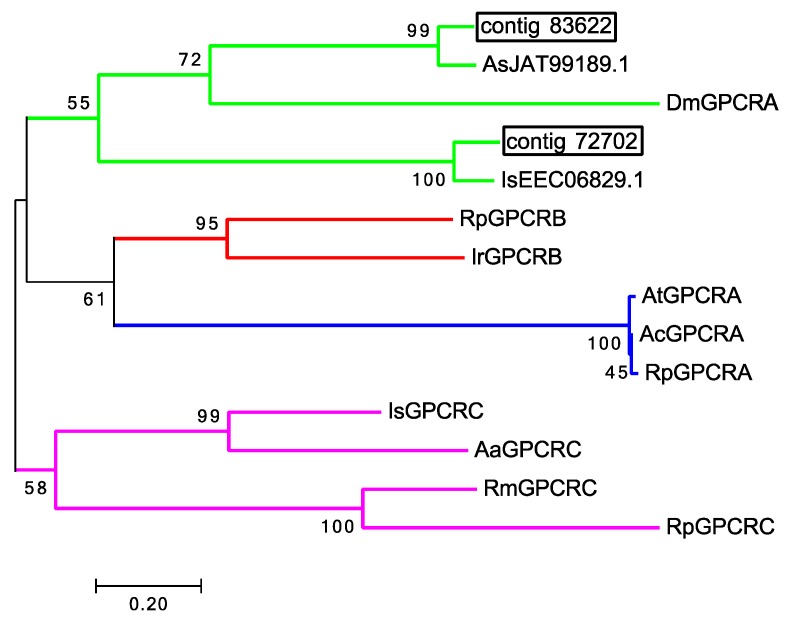
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic relationship of transcripts putatively encoding G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR) identified exclusively in the Haller’s organ spf transcriptome (contigs 72702, 83622) of unfed, virgin adult male Dermacentor variabilis with their top GenBank BLAST hits (lowest expect value; Table 3) and GPCRs of known clade annotation from Amblyomma americanum, Amblyomma cajennense, Amblyomma triste, Drosophila melanogaster, Ixodes ricinus, Ixodes scapularis, Rhipicephalus microplus, and Rhipicephalus pulchellus. The phylogenetic tree shows four clades, each represented by the following branch colors: blue = clade A; purple = clade C; green = clade D; red = clade B. Acronyms are as follows: first letter of the genus and species (Amblyomma americanum, Aa; Amblyomma cajennense, Ac; Amblyomma sculptum, As; Amblyomma triste, At; Drosophila melanogaster, Dm; Ixodes ricinus, Ir; Ixodes scapularis, Is; Rhipicephalus microplus, Rm; Rhipicephalus pulchellus, Rp) followed by the protein name (GPCR) and the letter of the associated clade (A, B, and C) or GenBank accession number (JAT99,189.1, EEC06829.1). Putative GPCR transcripts are boxed. The tree was constructed using Maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis and bootstrapping set to 500 iterations. Branch values listed are bootstrap percentages (percent confidence), scale set to 20%. A comprehensive list of acronyms and associated GenBank accession numbers are listed in Appendix A.