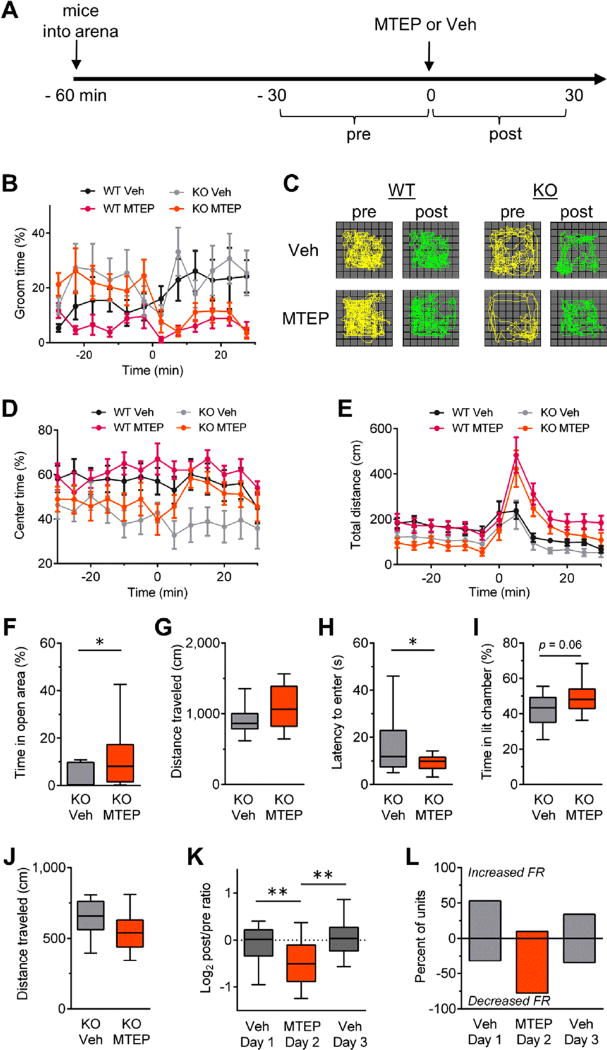
Figure 1.
Type 5 metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonism reduces obsessive-compulsive disorder–like behaviors in Sapap3 knockout (KO) mice. (A) Experimental design for evaluating the effects of MTEP (20 mg/kg, i.p.) in wild-type (WT) and Sapap3 KO mice in the open field (OF) (B–E). Injections of either MTEP or vehicle control (Veh) were given at time = 0 minutes. Drug modulation of behavior was evaluated for each genotype by comparing the 30-minute interval before (pre) and after (post) injection. WT vehicle n = 9, WT MTEP n = 14, KO vehicle n = 12, KO MTEP n = 12. (B) Grooming activity time course shows MTEP reduces basal grooming levels in Sapap3 KO mice but not WT mice. (C) Locomotor trajectories of representative WT and Sapap3 KO mice in the OF during 10-minute periods before and after injections of vehicle or MTEP. Time courses showing (D) center time and (E) total distance traveled in the OF. Time course data are presented as means ± SEMs. (F–J) Boxplots showing anxiolytic effects of MTEP in Sapap3 KO mice. For the elevated zero maze, (F) percentage of time spent in the open area and (G) locomotion (n = 17–18 per group). For the light-dark emergence, (H) latency to enter the brightly lit chamber, (I) percentage of time spent in the brightly lit chamber, and (J) locomotion (n = 15–17 per group). Boxplots showing (K) normalized change in striatal firing rate (FR) relative to preinjection period for striatal units recorded in vivo and (L) summary of units showing a change in firing rate during the postinjection period relative to the preinjection baseline with magnitudes >10%. Veh day 1, n = 201 units/4 mice; MTEP day 2, n = 231 units/4 mice; Veh day 3, n = 207 units/4 mice. Boxplots present median, upper, and lower quartiles, and upper and lower 90%. *p < .05, **p < .01. i.p., intraperitoneal.