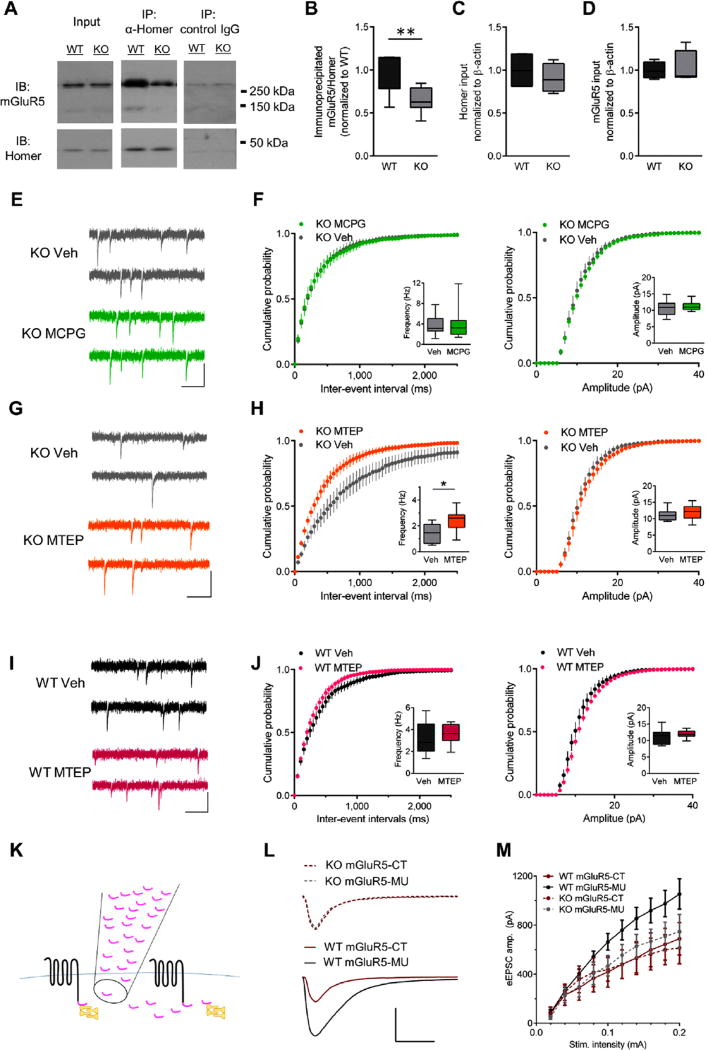
Figure 4.
Constitutive signaling contributes to ongoing type 5 metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR5) activity in Sapap3 knockout (KO) mice. (A) Representative Western immunoblots (IBs) from a littermate pair showing that Sapap3 deletion reduces co-immunoprecipitation (IP) of mGluR5 (monomers approximately 130 kDa, dimers approximately 260 kDa) with the long Homer isoform. Boxplots showing (B) significantly less mGluR5 co-immunoprecipitated with long Homer in KO relative to wild-type (WT) striatal extracts; however, input levels of (C) long Homer and (D) mGluR5 were not significantly different between WT and Sapap3 KO striatal extracts (n = 7–8 per group). (E) Representative traces and (F) summary data showing that MCPG (500 µmol/L) does not affect miniature excitatory postsynaptic current (mEPSC) frequency (left) or amplitude (right) in direct striatal projection neurons (dSPNs) in Sapap3 KO mice (n= 11 for both groups). (G) Representative traces and (H) summary data showing that MTEP significantly increases mEPSC frequency (left) but not amplitude (amp.) (right) in dSPNs in Sapap3 KO mice (n = 9 for both groups). (I) Representative traces and (J) summary data showing that MTEP (concentration 20 µmol/L) does not affect mEPSC frequency (left) or amplitude (right) in dSPNs in WT mice [vehicle (Veh), n= 7; MTEP, n= 9]. (E, G, and I) Scale bars = 25 pA, 200 ms. Boxplots present median, upper and lower quartiles, and upper and lower 90%. *p < .05, **p < .01. (K) Schematic showing that peptide corresponding to C-terminus of mGluR5 (mGluR5-CT; pink) competitively interferes with mGluR5 (black) and Homer (yellow) interactions. (L) Representative responses to 0.2-mA stimulation and (M) summary data demonstrate that mGluR5-CT reduces evoked EPSC amplitude in WT but not KO dSPNs (WT mGluR5-CT, n = 8; WT mGluR5-MU, n = 6; KO mGluR5-CT, n = 6; KO mGluR5-MU, n = 5). Scale bar = 500 pA, 20 ms. MU, mutated; Stim., stimulation.