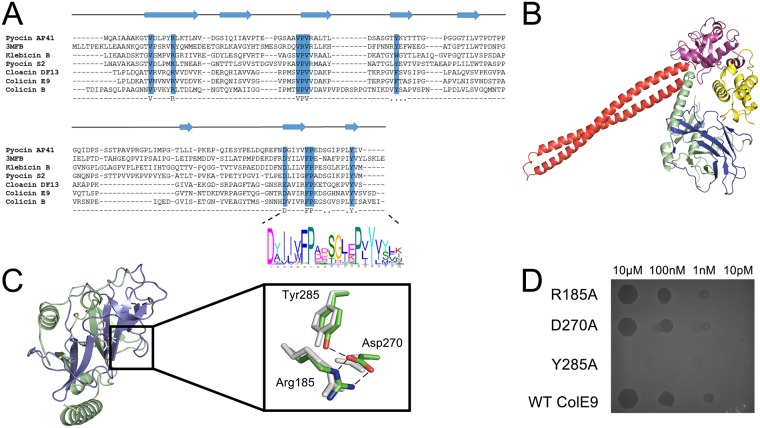
Fig 4. A conserved translocation motif was identified in all NBs.
a, Protein structure-based sequence alignment using PROMALS 3D indicates the conserved β-sheet secondary structure of a conserved domain identified in nuclease bacteriocins. Alignment features bacteriocins from E. coli (Colicin B, E9 and Cloacin DF13); Klebsiella pneumoniae (klebicin B), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Pyocin AP41) and the pyocin_s domain from Erwinia carotovora The DPY motif was identified using MEME and is shown by a LOGO plot at the C-terminal end of the T-domain. b, Crystal structure of colicin E9, with its constituent domains identified, in complex with its immunity protein Im9 (PDB code, 5EW5). c, The conserved segment of the T-domain (blue) is annotated as the pyocin_S domain in the PFAM database (PFAM 06958), which is usually part of a larger T-domain, annotated as PFAM 03515 (green). Inset, Alignment of resides at the core of PFAM 06958 showing a conserved hydrogen bond network formed between the residues of the DPY motif; Asp270 and Tyr285 (colicin E9 numbering) and Arg185 at the beginning of PFAM 06958. d, Cytotoxic plate killing assay of DPY motif mutations. 100-fold serial dilutions of colicin E9 and DPY motif alanine mutants were spotted onto a lawn of sensitive E. coli showing that only the Tyr285Ala mutant abolishes colicin activity.