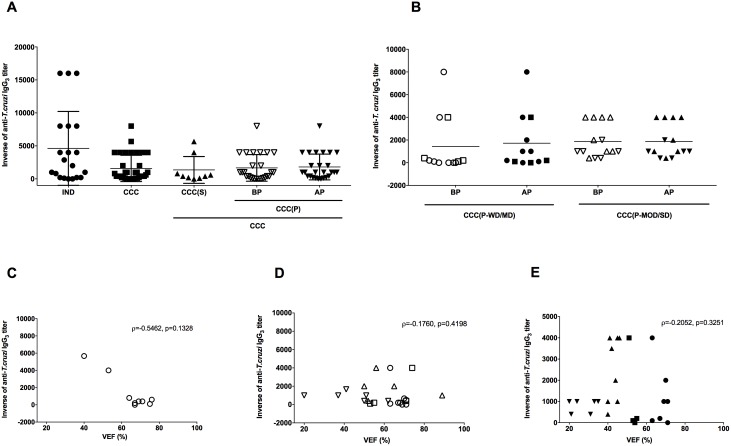
Fig 5. Reactivity of IgG3 for anti-T. cruzi antigen and correlation with ventricular ejection fraction in patients with Chagas disease.
(A) Inverse of the anti-T. cruzi IgG3 titers in sera of patients with chronic form of Chagas Disease in the indeterminate form of disease (IND), stable cardiomyopathy (CCC(S)), progressive cardiomyopathy (CCC(P)) before disease progression (BP) and progressive cardiomyopathy after disease progression (AP), respectively. The statistical analysis was calculated using ANOVA-one way plus Kruskal-Wallis post-test for multiple comparisons. (B) Inverse of anti-T. cruzi IgG3 titers in sera of patients with progressive cardiac form of Chagas disease (CCC(P) group) before and after disease progression sub-grouped according to the severity of cardiac commitment. Patients with progressive cardiac disease without (circles) or mild (squares) (CCC(P-WD/MD)) and moderate (triangles) or severe (inverted triangles) (CCC(P-MOD/SD)) cardiac dysfunction before (open symbols) and after (filled symbols) disease progression were represented. The statistical analysis was calculated using ANOVA-two way of repeated measures with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. The data of A and B were plotted as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). (C, D, and E) Correlation between anti-T. cruzi IgG3 titers and ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) in patients with the cardiac form of Chagas disease. (C) represents the correlation in patients with stable cardiac disease. (D) represents the correlation in patients with progressive cardiac disease before disease progression. Open circles, squares, triangles, and inverted triangles, represent CCC(P-WD), CCC(P-MD), CCC(P-MOD) and CCC(P-SD) patients, respectively. (E) represents the correlation in patients with progressive cardiac disease after disease progression. Filled circles, squares, triangles, and inverted triangles, represent CCC(P-WD), CCC(P-MD), CCC(P-MOD) and CCC(P-SD) patients, respectively. Spearman correlation was used to identify association between LVEF and anti-T. cruzi IgG3 levels.