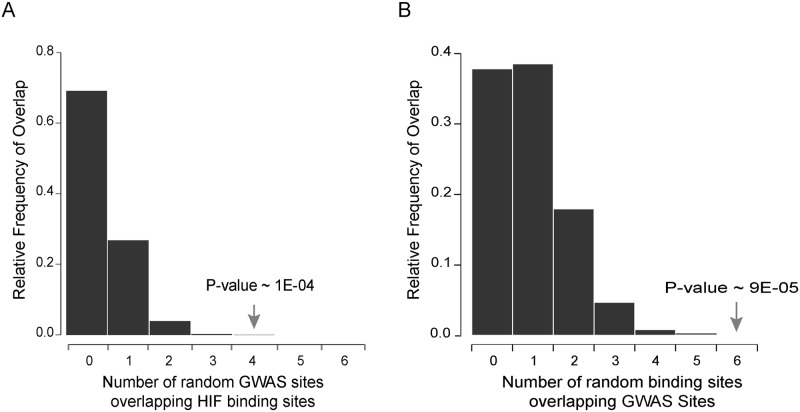
Fig 1. Non-random association between RCC GWAS loci and HIF-binding sites.
4 RCC GWAS loci overlapped with 6 HIF ChIP-seq peaks. A) To assess the significance of this overlap, the expected number of co-localization events was calculated by randomly shuffling the GWAS loci around the genome. This was repeated 100,000 times and the frequency distribution for the number of shuffled GWAS sites that overlapped a HIF-binding site was plotted. The probability of observing 4 or more GWAS loci overlapping a HIF ChIP-seq peak is 1x10-4 B) Conversely, HIF ChIP-seq peaks were randomly shuffled amongst all potential enhancer sites (as defined by the H3K27ac, H3K4me3, H3K4me1 in the same cell line 786-O), repeated 100,000 times and the frequency distribution for the number of shuffled HIF-binding sites that overlapped a GWAS site was plotted. The probability of observing 6 or more HIF-sites overlapping the GWAS sites is 9x10-5.