Abstract
We have undertaken an immunological and biochemical analysis of the most abundant soluble protein of previtellogenic Xenopus oocytes, 42S p48. We show that this protein shares immunological cross-reactivity with elongation factor 1 alpha (EF-1 alpha). Direct assays of both 42S fractions and purified 42S p48 show that this cross-reactivity is of functional significance since 42S p48, like EF-1 alpha, can transfer charged amino acids to ribosomes. We further demonstrate that 42S p48 is degraded soon after the onset of vitellogenesis, while the EF-1 alpha concentration remains essentially unchanged during this transition. These properties of 42S p48 are discussed with regard to its role in oogenesis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown D. D., Dawid I. B. Specific gene amplification in oocytes. Oocyte nuclei contain extrachromosomal replicas of the genes for ribosomal RNA. Science. 1968 Apr 19;160(3825):272–280. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3825.272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallius J., Rattan S. I., Clark B. F. Changes in activity and amount of active elongation factor 1 alpha in aging and immortal human fibroblast cultures. Exp Gerontol. 1986;21(3):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0531-5565(86)90068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppard N. J., Cramer F., Clark B. F. Identification of elongation factor 1 alpha from mouse liver. FEBS Lett. 1982 Aug 23;145(2):332–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80194-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis H., le Maire M. Thesaurisomes, a novel kind of nucleoprotein particle. Subcell Biochem. 1983;9:263–297. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-3533-7_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon L. K., Ford P. J. Regulation of protein synthesis and accumulation during oogenesis in Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1982 Oct;93(2):478–497. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90136-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D., Birnstiel M. L. Localization of amplified ribosomal DNA in the oocyte of Xenopus laevis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Aug 23;166(1):274–276. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90517-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonzi W. A., Katayama C., Leathers T., Sypherd P. S. Regulation of protein synthesis factor EF-1 alpha in Mucor racemosus. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1100–1103. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford P. J. Non-coordinated accumulation and synthesis of 5S ribonucleic acid by ovaries of Xenopus laevis. Nature. 1971 Oct 22;233(5321):561–564. doi: 10.1038/233561a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G. Differential synthesis of the genes for ribosomal RNA during amphibian oögenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jun;60(2):553–560. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.2.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda B. M., Roeder R. G. Association of a 5S gene transcription factor with 5S RNA and altered levels of the factor during cell differentiation. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90160-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mairy M., Denis H. Recherches biochimiques sur l'oogenèse. I. Synthèse et accumulation du RNA pendant l'oogenèse du crapaud sud-africain Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1971 Feb;24(2):143–165. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(71)90092-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
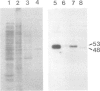
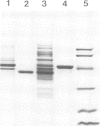
- Mattaj I. W., Lienhard S., Zeller R., DeRobertis E. M. Nuclear exclusion of transcription factor IIIA and the 42s particle transfer RNA-binding protein in Xenopus oocytes: a possible mechanism for gene control? J Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;97(4):1261–1265. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.4.1261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick W. C. Assays for eukaryotic protein synthesis. Methods Enzymol. 1979;60:108–123. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)60011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Brown D. D. A specific transcription factor that can bind either the 5S RNA gene or 5S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4170–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard B., Wegnez M. Isolation of a 7S particle from Xenopus laevis oocytes: a 5S RNA-protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):241–245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard B., le Maire M., Wegnez M., Denis H. Biochemical Research on oogenesis. Composition of the 42-S storage particles of Xenopus laevix oocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(2):359–368. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04802.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pingoud A., Urbanke C. Aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid binding site of the bacterial elongation factor Tu. Biochemistry. 1980 May 13;19(10):2108–2112. doi: 10.1021/bi00551a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Brown D. D., Engelke D., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. The binding of a transcription factor to deletion mutants of a 5S ribosomal RNA gene. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):665–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90429-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slobin L. I., Möller W. Purification of elongation factor 1 from embryos of Artemia salina. Methods Enzymol. 1979;60:685–703. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)60064-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hemert F. J., Amons R., Pluijms W. J., van Ormondt H., Möller W. The primary structure of elongation factor EF-1 alpha from the brine shrimp Artemia. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1109–1113. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01937.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]