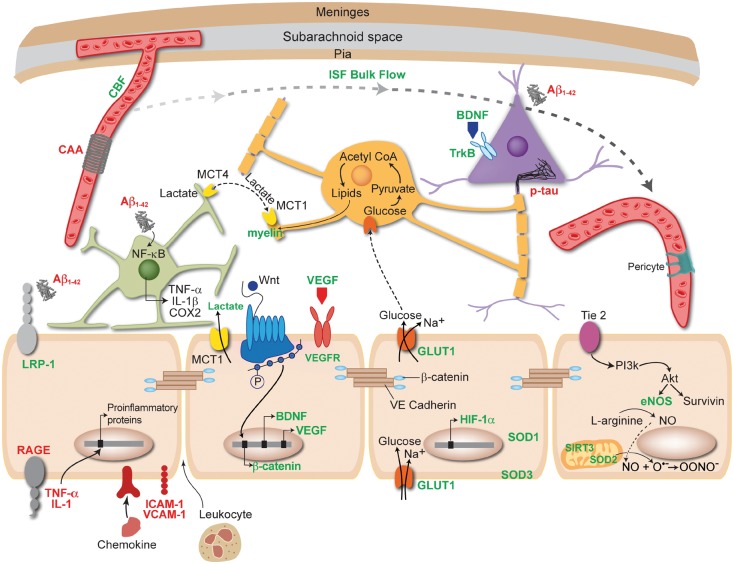
Figure 3.
Benefits of physical exercise (PE) act through or require a healthy, functional endothelium (beige cells). Items written in green are upregulated or improved by PE, while those written in red are decreased or downregulated. PE increases the bioavailability of NO, which is synthesized by eNOS in endothelial cells. PE improves quality and increases quantity of sleep, which can facilitate clearance of toxic protein aggregates including amyloid and hyperphosphorylated tau by the glymphatic system. This clearance prevents amyloid from activating astrocytes (green cell), and thus prevents proinflammatory mediators from entering blood vessels and damaging the endothelium. PE can increase LRP-1 and decrease RAGE found on endothelial cells. PE improves CBF, which can in turn decrease the amount of cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) around vessels and thus improve endothelial cell health. PE can decrease TNF-α and IL-1 levels in the periphery, as well as intracellular adhesion molecule (ICAM-1) and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1), which could prevent the transcription of proinflammatory proteins and entry of leukocytes across the BBB. PE increases the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD) enzymes and SIRT3 in mitochondria (peach cell), keeping ROS at low levels that will not negatively impact endothelial cell function. PE has been shown to upregulate GULT1 receptors found on endothelial cells, allowing more glucose into the brain. When glucose enters oligodendrocytes (orange cell) it is converted into lipids that are used to synthesize myelin. Another key component to myelin synthesis is lactate, which is upregulated by PE and enters the brain through MCT1 receptors found on endothelial cells. PE increases both brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) transcription in endothelial cells, as well as activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, which synthesizes β-catenin that is part of the structure of tight junctions between endothelial cells. These mechanisms may be important for neurogenesis and angiogenesis. Akt: protein kinase B; PI3K: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; SIRT3: sirtuin 3; HIF-1α: hypoxia-inducible factor 1α; IL-1β: interleukin 1β; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor alpha; COX-2: cycloxygenase 2.