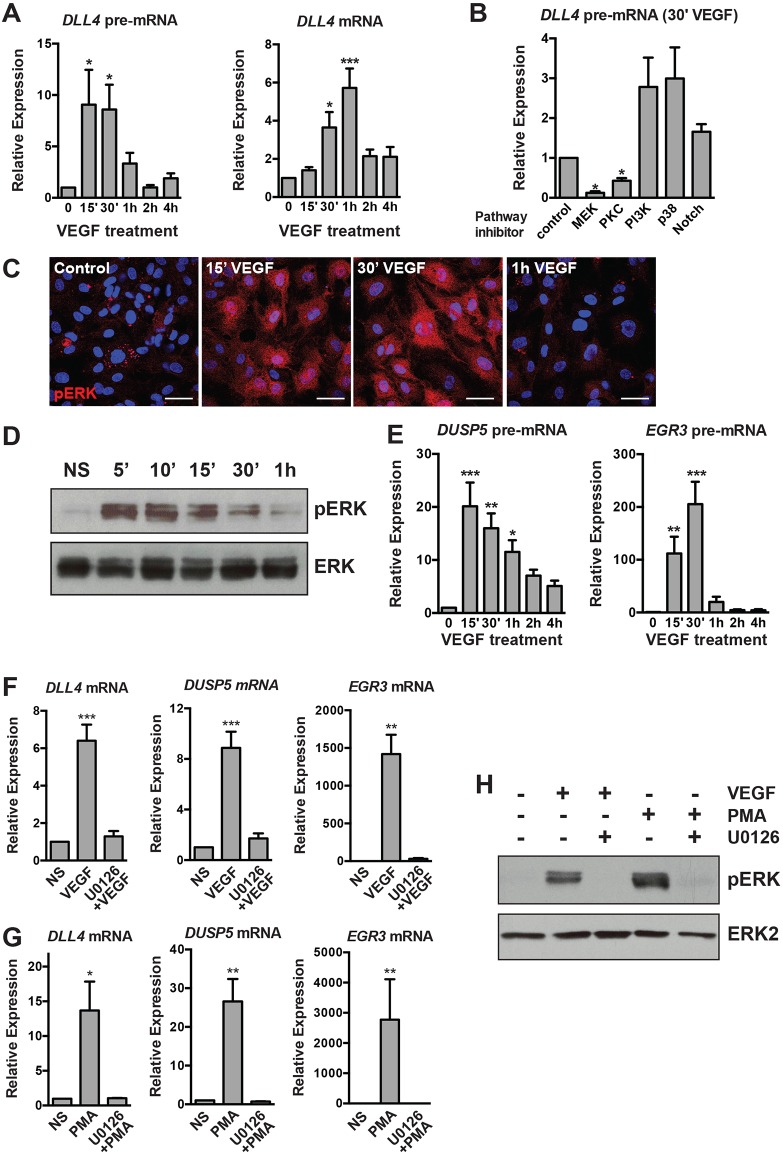
Fig. 1.
Transcriptional activation of DLL4 and other angiogenic genes in response to VEGF stimulation requires active MAPK/ERK signaling. (A) Kinetics of DLL4 transcriptional activation (as measured by qRT-PCR of unspliced DLL4 pre-mRNA) and expression of mature DLL4 mRNA in HUVECs treated with VEGF (n=7). (B) Inhibition of the MAPK pathway (by PKC and MEK inhibitors) ablates induction of DLL4 pre-mRNA (measured 30′ after VEGF treatment by qRT-PCR), whereas Notch inhibition has no effect (n=3). Expression is relative to vehicle-treated, VEGF-stimulated cells. (C) Kinetics of MAPK/ERK activation as detected by pERK (red) immunofluorescence in HUVECs. Blue, DAPI staining. Scale bars: 40 μm. Representative experiment of three. (D) Kinetics of pERK in VEGF-stimulated cells assessed by western blot. Total ERK is included as a loading control. Representative experiment of two. (E) Kinetics of DLL4 pre-mRNA induction are similar to known MAPK/ERK-dependent genes (EGR3, DUSP5) (n=3). (F) Induction of DLL4, DUSP5 and EGR3 by VEGF is abrogated in cells pre-treated with the MEK inhibitor U0126 (n=5). (G) Induction of DLL4, DUSP5 and EGR3 by PMA is abrogated in cells pre-treated with the MEK inhibitor U0126 (n=4). (H) Western blot demonstrating the efficacy of U0126 pre-treatment of VEGF- or PMA-treated cells. pERK is not induced in U0126 pre-treated cells (n=1). NS, non-stimulated.