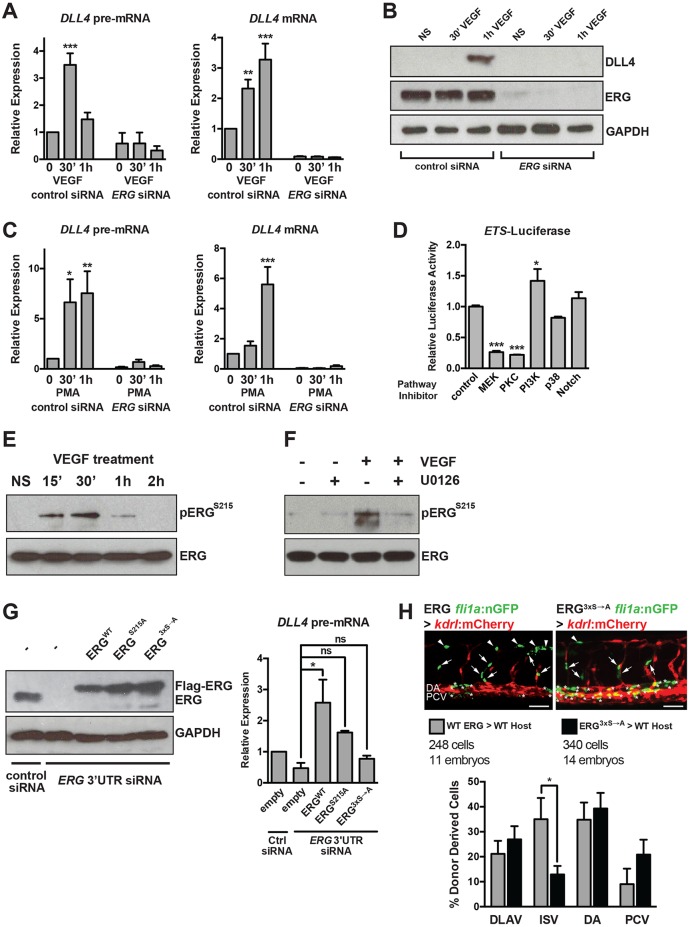
Fig. 3.
VEGF/MAPK signaling stimulates ERG transcriptional activity to induce DLL4 expression. (A) VEGF induction of DLL4 transcription (as assessed by qRT-PCR measurement of DLL4 pre-mRNA) and mature DLL4 mRNA expression in HUVECs requires ERG (n=4). (B) VEGF induction of DLL4 protein expression requires ERG. Representative experiment of three. (C) Induction of DLL4 transcription by PMA, an activator of MAPK/ERK signaling, requires ERG (n=4). (D) ETS activity (as assessed by activity of an 8× concatamer of an ETS element driving luciferase expression) in BAECs is suppressed by MEK or PKC inhibition. Triplicate determinations from a representative experiment of three. (E) ERG is phosphorylated at S215 in response to VEGF stimulation (15-30′) in HUVECs. Representative experiment of two. (F) VEGF-induced phosphorylation of ERG requires MEK activity. Representative experiment of two. (G) ERG was knocked down using siRNAs directed to the 3′ UTR, followed by overexpression of Flag-tagged wild-type (WT) or mutant (S215A or S96A;S215A;S276A, indicated as 3xS→A) ERG. ERG western blot indicates restoration of expression using electroporated constructs (a representative experiment of three is shown). DLL4 expression as assessed by qRT-PCR of pre-mRNA after 1 h of VEGF treatment (n=3). (H) Representative images of transplanted cells from Tg(fli1a:nls-GFP) embryos injected with wild-type or mutant ERG mRNA into Tg(kdrl:mCherry) embryos. Arrows and asterisks indicate endothelial cells that are donor derived. Quantification of cellular position is shown below (n=248 cells from 11 embryos for wild type and n=340 cells from 14 embryos for mutant). Scale bar: 50 µm. DA, dorsal aorta (asterisks); DLAV, dorsal longitudinal anastomotic vessel (arrowheads); ISV, intersomitic vessel (arrows); NS, non-stimulated; PCV, posterior cardinal vein.