Fig. 11.
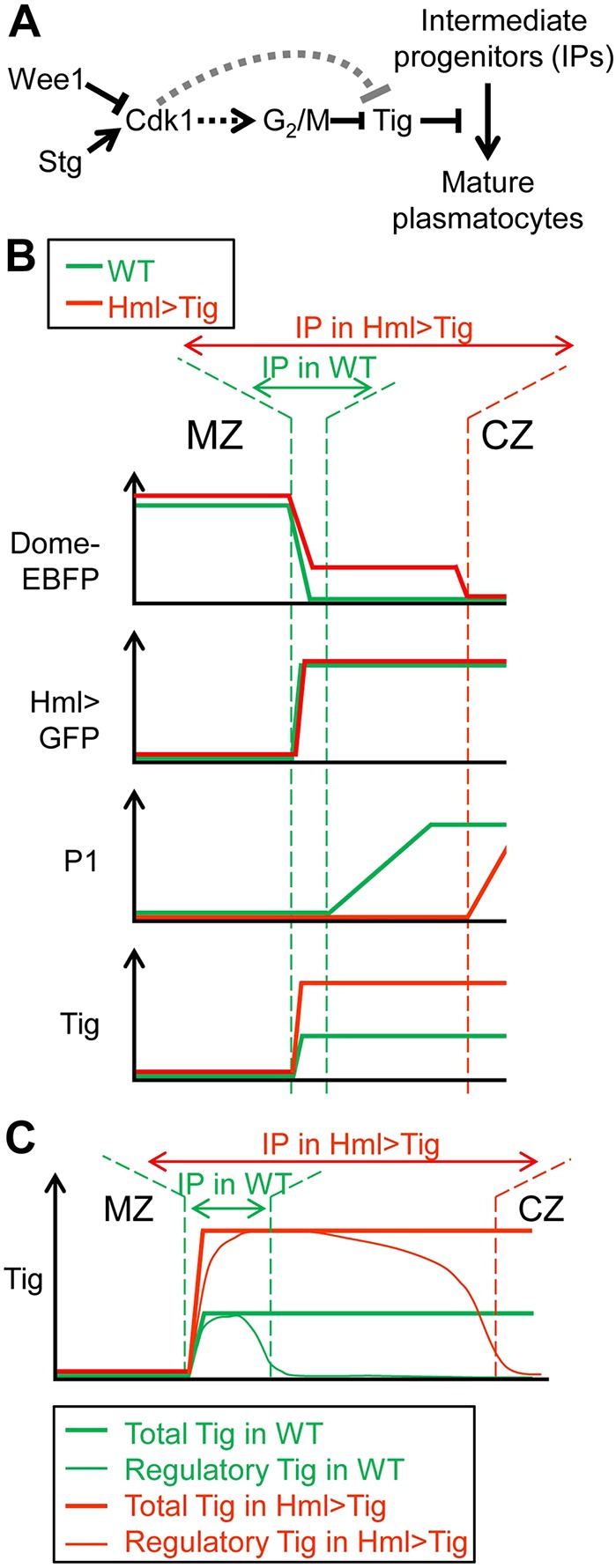
Working model of the regulation of plasmatocyte maturation by Tig and cell cycle regulators. (A) Genetic pathway controlling plasmatocyte differentiation. Tig and Wee1 inhibit the transition from IPs to plasmatocytes, while Stg accelerates it. Tig is epistatic to Wee1 and Wee1 activates Tig expression. Wee1 and Stg could affect Tig though their common target Cdk1 and may affect Tig expression by altering the G2/M transition. Alternatively, they could act on Tig transcription independently of the cell cycle. (B) Summary of the expression levels of different proteins across the MZ and CZ in wild-type and Hml>Tig PLs at the mid/late-3rd instar stage. There is a dramatic expansion of the domain containing IPs in Hml>Tig, i.e. cells that are Dome+/Hml+/P1−. (C) A speculative model for a ‘regulatory’ pool of Tig promoting the IP cell fate. Tig protein is detected at uniform levels throughout the CZ (Zhang et al., 2014), but we propose that newly synthesized Tig protein forms a regulatory pool that is enriched in the IPs, where it acts as a brake on plasmatocyte maturation.
