Fig. 7.
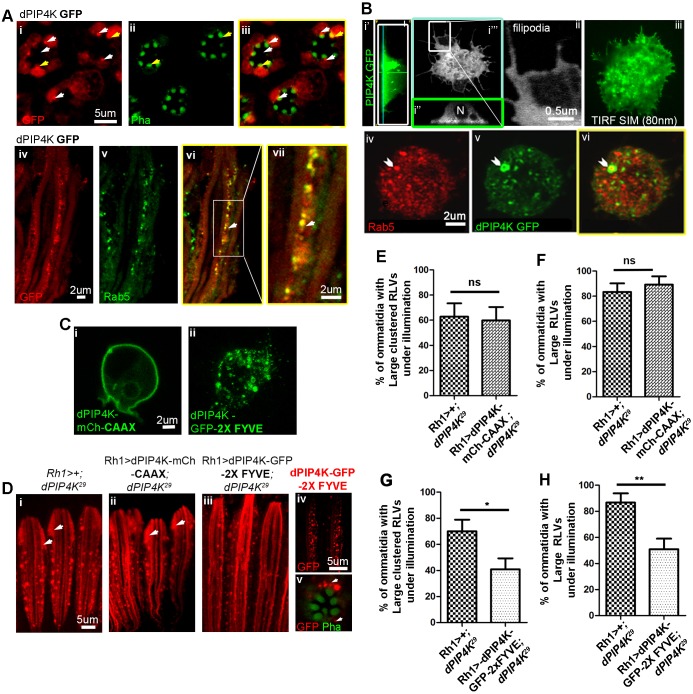
PIP4K::GFP localizes to and is required in early endosomal compartments during CME. (A) (i-iii) Transverse sections of PRs at 90% pupal development from Rh1>PIP4K::GFP flies reared under illumination. PIP4K::GFP partly localizes to the rhabdomere (APM) (stained with phalloidin, green) as indicated by the white arrows. PIP4K::GFP also localizes to the cell body of the PRs and occasionally is visible as distinct punctae close to the base of rhabdomere. (iv–vii) Longitudinal sections of ommatidia, showing the PIP4K::GFP (green) punctae colocalizing with early endosomal Rab5 (red) compartments. (B) Localization of PIP4K::GFP in S2R+ cells. (Bi′,i″) Longitudinal sections of S2R+ cells transiently expressing PIP4K::GFP, showing it to be broadly distributed, enriched close to PM near the coverslip and excluded from the nucleus (N). (Bi′″,ii) Confocal section showing that PIP4K::GFP is localized close to plasma membrane, and is occasionally visible as punctae and in the filopodial extensions. (Biii) TIFR-SIM image showing PIP4K localizing close to the PM (80 nm TIRF field). (Biv–vi) Occasionally PIP4K::GFP was present next to early endosome compartments marked by Rab5 (red) as highlighted by the chevrons. (C) Colocalization of CAAX-tagged PIP4K (dPIP4K-mCh-CAAX) (i) and 2×FYVE-tagged PIP4K::GFP (dPIP4K-GFP-2X FYVE) (ii) verified in S2 cells. (D) RLVs (red) in Rh1>+; PIP4K29 (i), Rh1>PIP4K-mCherry-CAAX; PIP4K29 (ii) and Rh1>PIP4K::GFP-2X FYVE; PIP4K29 (iii) lines. Localization of PIP4K::GFP–2XFYVE in longitudinal sections (iv) and transverse sections (v) of PRs as distinct puncta or vesicles. (E–H) Quantification of the percentage of ommatidia containing large clustered RLVs and large RLVs in Rh1>PIP4K-mCherry-CAAX; PIP4K29 and Rh1>PIP4K::GFP-2X FYVE; PIP4K29 lines with respect to that in PIP4K29. PIP4K::GFP–2XFYVE partially suppresses formation of large clustered RLVs and large RLVs in PIP4K29 flies. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ns, not significant.