Fig. 1.
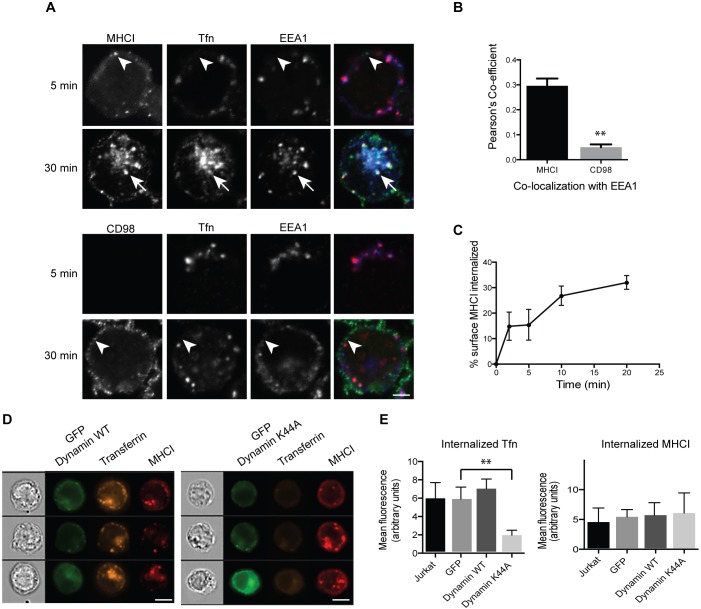
Jurkat T cells internalize CIE cargo separately from transferrin, in a dynamin-independent manner, at a rate of 2% per minute. (A) Cells were incubated at 37°C with antibodies to MHCI or CD98 and Alexa Fluor 633-conjugated transferrin for 5 or 30 min. Bound surface antibodies were removed by treating cells with a low pH buffer for 8 s prior to fixation. Cells were immunolabeled with antibodies to EEA1, and fluorescent secondary antibodies were used to detect internalized MHCI and CD98 antibody. MHCI is in puncta that are distinct from transferrin-containing endosomes (arrowheads) at 5 min, indicating an entry mechanism distinct from CME. Note that at 30 min, MHCI and transferrin meet in a common endosome (arrows) and in the ERC. CD98 is in a distinct endosome (arrowhead) that does not colocalize with transferrin. Scale bar: 3 µm. (B) The Pearson's correlation coefficient shows a significant difference between the correlation of MHCI with EEA1, as compared to CD98 with EEA1, at the 30 min time point. Shown is the mean±s.e.m. of three experiments, with at least 42 cells measured in each experiment. **P<0.01 (unpaired t-test). (C) Cells were incubated at 4°C with antibodies to MHCI. Cells were washed, returned to warm medium, fixed at indicated time points, and remaining surface antibody detected by fluorescent secondary antibodies and imaging flow cytometry. MHCI enters cells at a rate of ∼2% per minute. Shown is the mean±s.e.m. of four experiments. (D,E) Cells were transfected with GFP-tagged wild-type (WT) or K44A mutant dynamin, and then incubated at 37°C with antibodies to MHCI and Alexa Fluor 594-conjugated transferrin for 30 min. Bound surface antibodies were removed by treating cells with a low pH buffer for 8 s prior to fixation. (D) Sample images from imaging flow cytometry showing that there is a decrease in internalized transferrin in cells expressing dynamin K44A. Scale bars: 7 µm. (E) Quantification of internalized transferrin (Tfn) and MHCI by flow cytometry. Shown is the mean±s.e.m. of four experiments (2000 cells scored/treatment). GFP–dynamin-K44A significantly reduces transferrin internalization but not MHCI internalization. **P<0.01 (unpaired t-test).