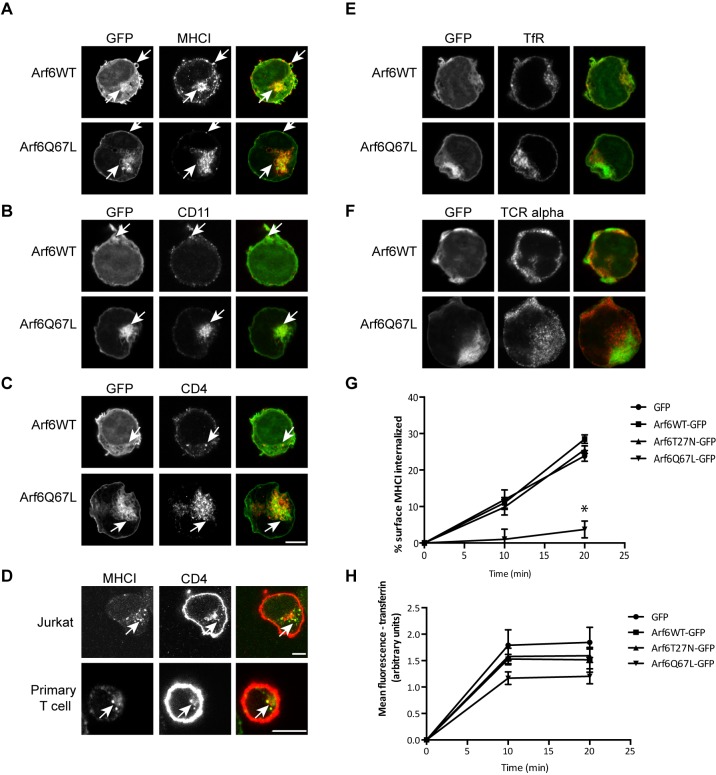
Fig. 3.
Arf6 colocalizes with CIE cargo proteins that are important for T cell activation and Arf6Q67L inhibits CIE in Jurkat T cells. Cells were transiently transfected with Arf6WT–GFP or Arf6Q67L–GFP. After fixation, the steady state distribution of cargo proteins was assessed with antibodies, followed by labeling with Alexa Fluor 594-conjugated secondary antibodies. MHCI (A), CD11 (LFA-1) (B), and CD4 (C) colocalize with Arf6WT and Arf6Q67L. CME cargo proteins transferrin receptor (E) and T cell receptor α (F) do not colocalize with Arf6-positive membranes. Scale bars: 3 µm. (D) Jurkat T cells and primary T cells were incubated with antibodies to MHCI for 30 min, treated with a low pH wash, then fixed and stained with antibodies to CD4, followed by use of Alexa Fluor 488-secondary antibody to detect MHCI and Alexa Fluor 594-secondary antibodies to detect CD4. Scale bars: 5 µm. Arrows highlight cargo-containing endosomes. (G,H) Cells were chilled to 4°C and incubated with antibodies to MHCI (G) or fluorescently conjugated transferrin (H). Cells were rinsed and warmed for the indicated times to allow internalization of antibody-bound MHCI and transferrin. Remaining surface MHCI and internalized transferrin were measured by using imaging flow cytometry. Expression of Arf6Q67L inhibits internalization of the CIE cargo protein MHCI but not the CME cargo protein transferrin receptor, as measured by determining transferrin internalization. Shown are the mean±s.e.m. for four experiments. For the 20 min time point, cells expressing Arf6Q67L internalized less MHCI than GFP controls. *P<0.05 (unpaired t-test).