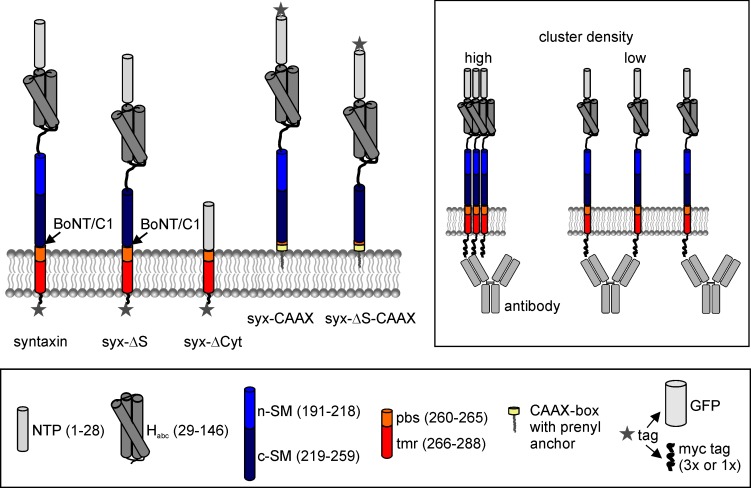
Figure 1. Domain structure of syntaxin 1A and deletion constructs.
Pictogram illustrating the constructs’ domain structure, the botulinum neurotoxin C1 (BoNT/C1) cleavage site and the tag positions. In case of the CAAX constructs, the TM domain and parts of the pbs were exchanged for a CAAX box from K-Ras that after prenylation anchors the construct to the plasma membrane. Lower legend; N-terminal short peptide (NTP, grey), globular N-terminal domain (Habc; dark grey), SNARE motif section divided into an N- and a C-terminal part (n-SM and c-SM in blue and dark blue, respectively), polybasic stretch (pbs; orange) and the remaining transmembrane region (tmr; red), and the prenylated CAAX-box (yellow). Two types of tags were used, a monomeric variant of GFP or a triple myc-tag, both fused via a 12 amino acid linker to the extracellular site. The myc-tags were attached to the extracellular site to minimise the possibility of intracellular conformational changes masking the epitope of the myc-tag. The CAAX constructs carry the myc-tag at the N-terminus and were comparatively studied with N-terminally myc-tagged syntaxin (not shown). Upper right box, accessibility of the antibody to the myc-tag depends on the molecule packing density.