Figure 2.
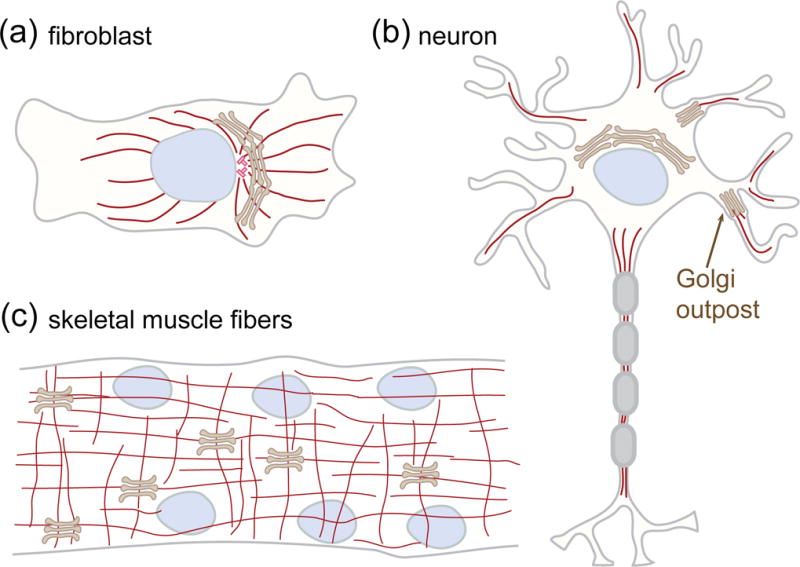
Golgi stacks in proliferating and differentiated mammalian cells. (a) Golgi ribbon in fibroblasts. The stacks are laterally linked together into a continuous ribbon that localizes in the perinuclear and pericentriolar region of the cell. (b) Golgi outposts in neurons. During neuronal differentiation, some stacks detach from the somatic ribbon and relocated to dendrites. These Golgi outpost function as sites for local secretion and microtubule nucleation to regulate dendrite outgrowth. (c) Golgi stacks in muscle fibers. In skeletal muscle fibers, the ribbon is broken up into stacks. Microtubules originating from the nuclear membrane and from Golgi stacks form a grid-like network.
