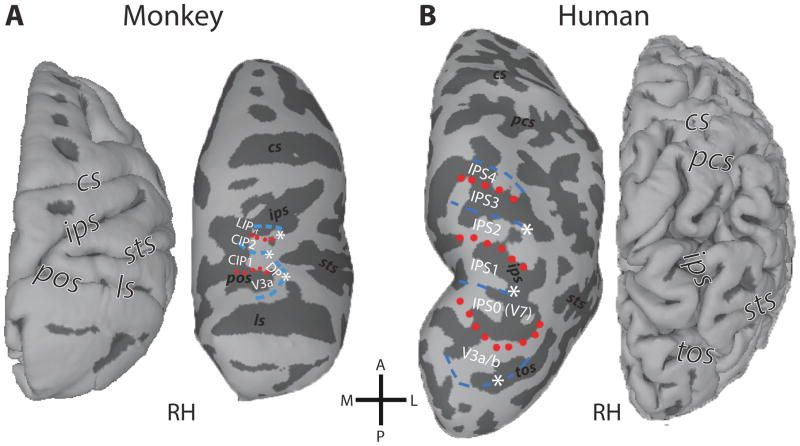
Figure 1. Topographic organization of primate PPC.
Comparison of the fMRI-defined retinotopic organization of dorsal occipital and parietal cortex in both monkeys (A) and humans (B). Lines denote areal boundaries formed by phase angles at or close to the upper (red, dotted) or lower (blue, dashed) vertical meridian. Surfaces are rendered with anterior (A) up, posterior (P) down, medial (M) left, and lateral (L) right. Major sulci are labeled in each view: cs, central sulcus; pcs, postcentral sulcus; ips, intraparietal sulcus; ls, lunate sulcus; pos, parieto-occipital sulcus; tos, transverse occipital sulcus. (After: Arcaro, et al., 2011)