Fig. 4.
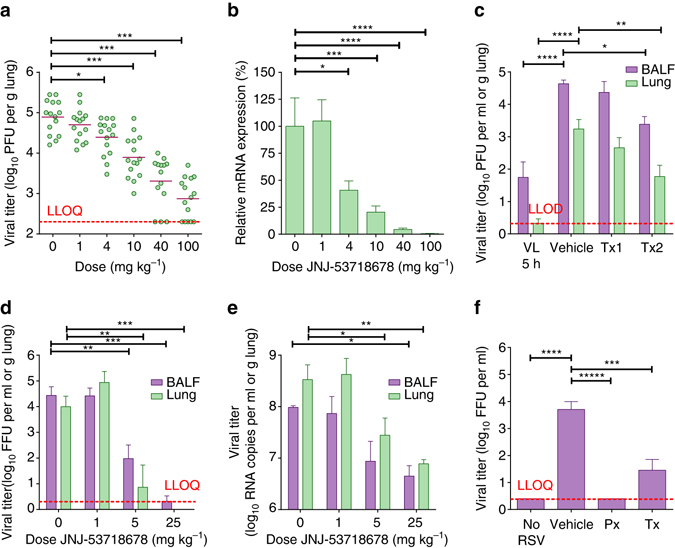
Administration of RSV fusion inhibitors reduces infection in animal models. a Dose-dependent inhibition of infectious RSV titer in lavaged-lung tissue of male, 6–8-week-old infected cotton rats treated with a single dose of JNJ-53718678 1 h before infection. Shown on the graphs are the individual data points measured (green circles); bars represent mean values (n = 15). b Relative dose-dependent inhibition of RSV mRNA expression in lung tissue of male, 6–8-week-old infected cotton rats treated with a single dose of JNJ-53718678 1 h before infection. mRNA expression in cotton rats treated with different single doses of JNJ-53718678 was calculated relative to the vehicle-treated animals (set as 100 %). Green bars represent average values + s.e.m. (n = 15). c Inhibition of the infectious RSV titer in BALF (purple bars) and lavaged-lung tissue (green bars) of 5–15-week-old infected cotton rats of both sexes treated with a single dose (Tx1; n = 4) or multiple once-daily doses (Tx2; n = 10) of 40 mg kg−1 JNJ-53718678 starting 24 h after infection. Titers of compound-treated animals were compared to the titers in animals treated with vehicle only (vehicle; n = 9) on Day 4 after infection. As a positive control for viral growth in the lungs of animals in the absence of treatment with JNJ-53718678, RSV titers were determined in BALF and lavaged-lung tissue at 5 h after intranasal inoculation (VL 5 h; n = 10) and compared to the titers on Day 4. Bars represent average values + s.e.m. d, e Inhibition of the infectious RSV titer d and RSV viral RNA levels e in BALF (purple bars) and lavaged-lung tissue (green bars) of 1–3-day-old infected neonatal lambs of both sexes treated once daily with 1 (n = 4), 5 (n = 3), or 25 (n = 3) mg kg−1 of JNJ-53718678 or with vehicle only (0; n = 3) as indicated on the x-axis. Bars represent average values + s.e.m. f Treatment-dependent inhibition of infectious RSV titer in BALF of 1–3-day-old infected neonatal lambs of both sexes treated once daily with 25 mg kg−1 JNJ-49214698 starting 24 h before (Px; n = 4)) or 72 h after infection (Tx; n = 5) and compared to the titer in vehicle only-treated (n = 4) or non-infected (n = 5) animals. Red dotted line indicated the lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) or detection (LLOD) of the respective assays. Statistical analysis in all panels was performed by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post hoc. *p-value < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001
