Figure 1.
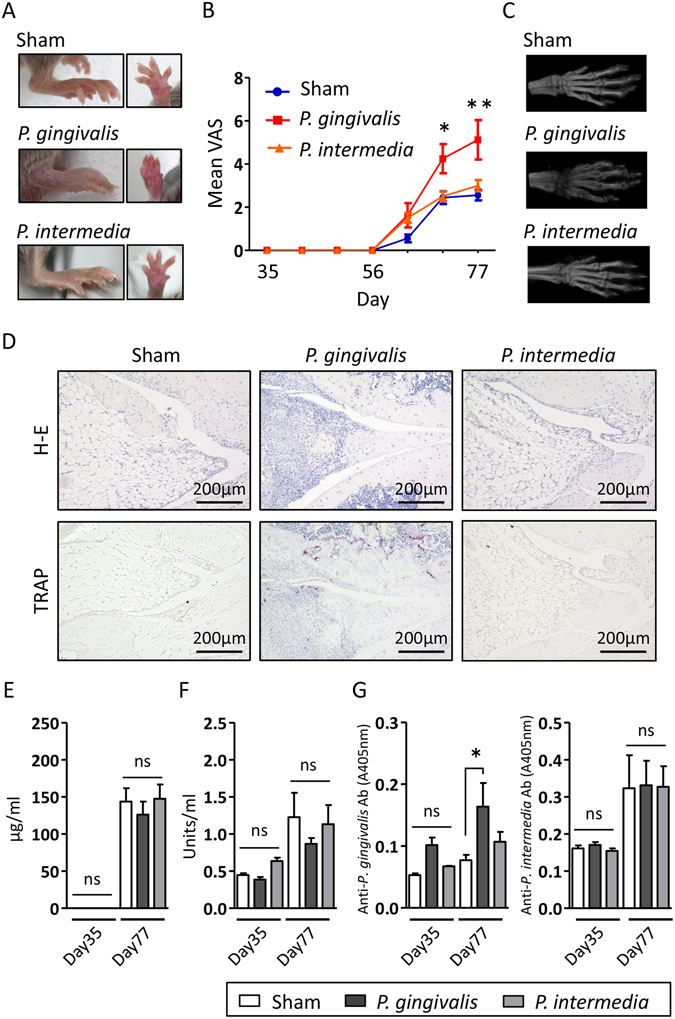
Effect of P. gingivalis administration on clinical features and serum levels of antibodies in a CIA model. (A) Representative image of the hind paw of sham-, P. gingivalis-, and P. intermedia-administered mice following CII immunisation. (B) Visual assessment score (VAS) of sham-, P. gingivalis-, and P. intermedia-administered mice. (C) Micro-computed tomographic appearance of the paws of sham-, P. gingivalis-, and P. intermedia-administered mice. (D) Histological analysis of the knee joints of sham-, P. gingivalis-, and P. intermedia-administered mice. Sections were stained with haematoxylin and eosin, and tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase in combination with haematoxylin. Serum levels of anti-CII antibodies (E), anti-cyclic citrullinated protein (CCP) antibodies (F), and IgG antibodies against P. gingivalis W83 and P. intermedia ATCC 25611 (G) were compared between sham-, P. gingivalis-, and P. intermedia-administered mice. Sera were obtained immediately before immunisation (day 35) and after induction of CIA (day 77). Data represent the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) (N = 6 for (A,B,E,F and G). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni corrections for multiple comparisons.
