Figure 3.
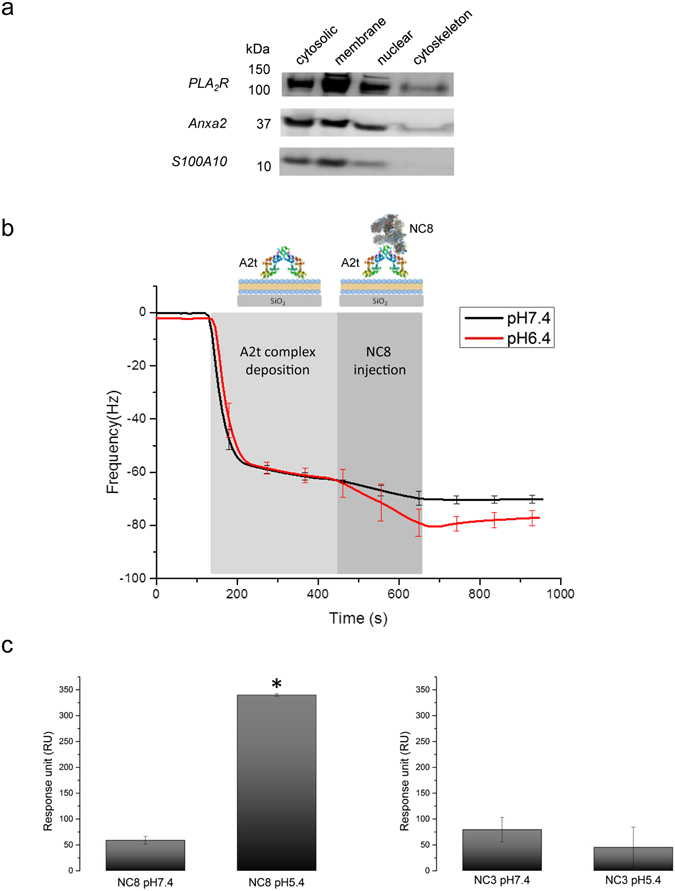
PLA2R binding to A2t complex is increased in a pH-dependent manner. (a) Western blot analysis of fractionated cellular protein from over-expressing PLA2R podocytes. Podocytes proteins were fractionated using the subcellular protein extraction kit. Each extracts were analysed by western blotting using antibodies against PLA2R, Anxa2 and S100A10 (full length blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. 3). The results show an enrichment of all three blotted proteins in the membrane and membrane organelles fraction. (b) The complex formation between PLA2R and A2t at different pHs was determined in real time using quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation (QCM-D). A2t complex was injected onto a preformed lipid bilayer. A2t protein bound to the lipids and formed a stable layer. PLA2R NC8 incubated either in buffer pH 6.4 or pH 7.4 was then added while monitoring the frequency change. An increase in bound PLA2R NC8 to A2t complex was detected in acidic pH 6.4 compared to neutral pH 7.4. (c) Measurements of the binding level of PLA2R NC8 and NC3 to S100A10 at different pHs using SPR. A maximum binding was obtained between PLA2R NC8 and S100A10 at pH 5.4 confirming the QCM-D data. The different pHs did not significantly affect the binding of NC3 to S100A10. Statistical significance was evaluated using ANOVA test. *P < 0.05.
