Figure 3.
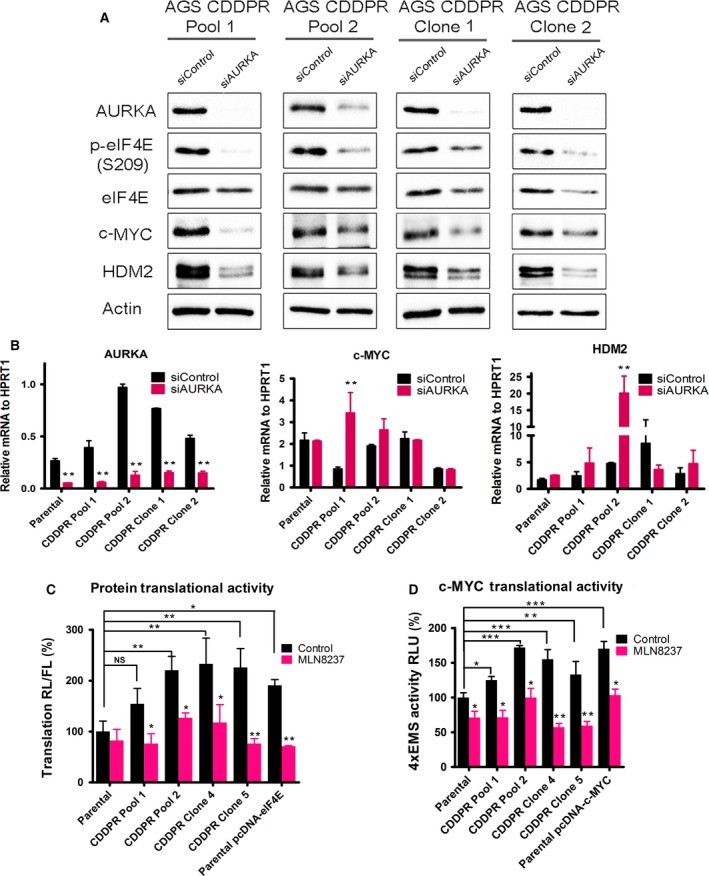
Genetic knockdown of AURKA reduces phosphorylation of eIF4E and protein levels of its downstream effectors in CDDP‐resistant cells. AGS CDDPR Pool 1, AGS CDDPR Pool 2, AGS CDDPR Clone 1, and AGS CDDPR Clone 2 cells were transfected with control siRNA (siControl) or siRNA specific for AURKA (siAURKA) for 48 h. Cell lysates and total RNA were subjected to western blot (A) and real‐time RT‐PCR (B) analyses, respectively. The data showed that knockdown of AURKA led to decreased p‐eIF4E (S209), c‐MYC, and HDM2 protein levels, but did not decrease mRNA expression of the corresponding encoding genes in CDDP‐resistant cells. Gel loading was normalized for equal β‐actin. HPRT1 housekeeping gene was used as the internal control for PCR. (C) AGS Parental, AGS CDDPR Pool 1, AGS CDDPR Pool 2, AGS CDDPR Clone 1, and AGS CDDPR Clone 2 cells were transfected with luciferase reporter plasmid (pcDNA3‐rLuc‐Polio IRES‐fLuc). Cells were treated with MLN8237 (0.5 μm) for 24 h. The rate of cap‐dependent translation was defined as the ratio of renilla to firefly luciferase activities. (D) AGS Parental, AGS CDDPR Pool 1, AGS CDDPR Pool 2, AGS CDDPR Clone 1, and AGS CDDPR Clone 2 cells were transfected with 4 × EMS c‐MYC reporter. Cells were treated with MLN8237 (0.5 μm) for 24 h. Luciferase activity was determined as described in Materials and methods. The results showed that the basal level of cap‐dependent translation activity and c‐MYC transcription activity in AGS CDDPR cells are significantly higher than in AGS Parental cells. ***P < 0.001. Additionally, treatment with MLN8237 significantly reduced cell cap‐dependent translation or 4xEMS c‐MYC Luciferase activity in comparison with the no‐treatment control group. Transient transfections with pcDNA‐eIF4E (C) or pcDNA‐c‐MYC (D) were included as controls. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
