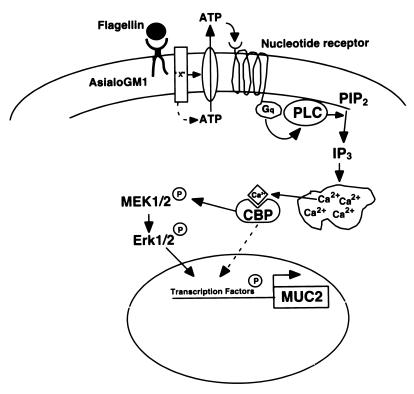
Figure 7.
Cartoon depicting events in flagellin-triggered host cell signaling. Flagellin binds to asialoGM1, a membrane glycolipid, which causes the extracellular release of ATP, which then binds to a nucleotide receptor. Downstream events include G-protein activation, the cleavage of PIP2 by PLC, the formation of IP3, Ca2+ mobilization, the phosphorylation of MEK 1/2 and Erk 1/2 [via an unknown calcium binding protein (CBP)], and mucin (MUC 2) transcription. Flagellin-induced signaling bifurcates after Ca2+ mobilization, with ≈50% of the response giving rise to downstream events that are Erk dependent whereas the remaining 50% is Erk independent.