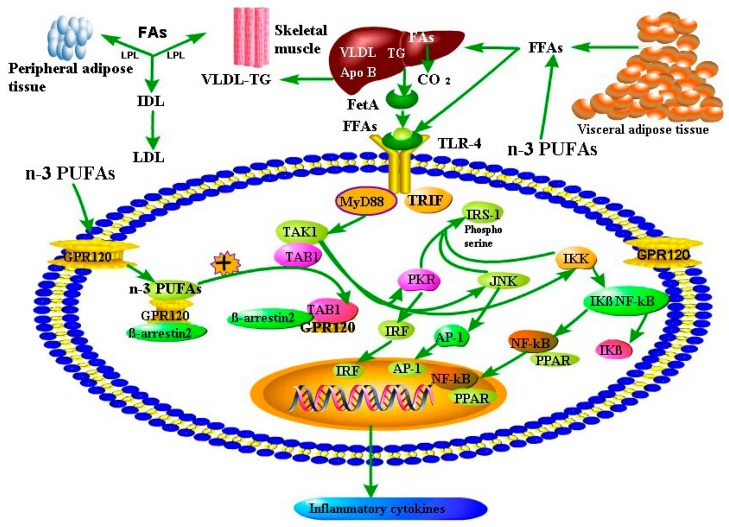
Figure 6.
The underlying mechanisms of n-3 PUFAs protecting metabolic syndrome. Dysfunctions of lipid metabolism and inflammation contribute to metabolic syndrome. The high lipolytic rate in visceral adipose provides the liver with large amounts of FFAs. Impaired fat oxidation stimulates fatty acid esterification into TG, together with an augmented synthesis of Apo B, cholesterol and the secretion of VLDL. Moreover. FFAs may result in the activation of TLR4 pathways. Fet-A functions as an adaptor between FFAs and TLR4 signaling in lipid-induced inflammation. FFAs stimulate TLR-4 signaling by binding Fet-A, which then binds TLR-4. JNK, IKK, and PKR play important roles in upregulating the transcription factors (including AP-1, NF-κB, and IRF), resulting in the production of inflammatory cytokines. Moreover, these kinases can inhibit insulin signaling via serine phosphorylation of IRS-1. n-3 PUFAs modulate lipid and lipoprotein metabolism. Reduced VLDL production in the liver largely results from decreased availability of FFAs released from adipose stores, together with suppression of lipogenic genes and induction of genes involved in fatty acid oxidation. Inhibition of FFAs released from visceral adipose tissue due to a higher circulating n-3 PUFAs concentration, the TLR-4/MyD88 signaling pathway would be suppressed. Accordingly, the expression levels of PKR, IKK, JNK are inhibited. Finally, the release of inflammatory cytokines from adipocytes will be decreased. PPAR are transcription factors and regulate gene expression. PPAR are activated by non-covalent binding of ligands, such as n-3 PUFAs and eicosanoid mediators. Through activation of PPAR, n-3 PUFAs are able to regulate metabolism and other cell and tissue responses, including adipocyte differentiation and inflammation. Activation of GPR120 by n-3 FUFAs through binding β-arrestin 2 and TAB1 could inhibit pro-inflammatory pathways. Abbreviations: PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acid; FFAs, free fatty acids; Apo B, apolipoprotein B; IDL, intermediate-density lipoprotein; LPL, lipoprotein lipase; TAG, triacylglycerol; FA, fatty acid; Fet-A, Fetuin-A; TLR-4, toll-like receptor 4; AP-1, activator protein-1; IKK, inhibitor of NF-κB kinase; IRF, interferon regulatory factor; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; IRS-1, insulin receptor substrate 1; JNK, c-jun N-terminal kinase; PKR, protein kinase R; TRIF, TIR domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β; MyD88, myeloid differentiation factor 88. TAK1, transforming growth factor-activated kinase 1; TAB1, transforming growth factor-β activated kinase 1 binding protein 1; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; GPR120, G-protein-coupled receptor 120.