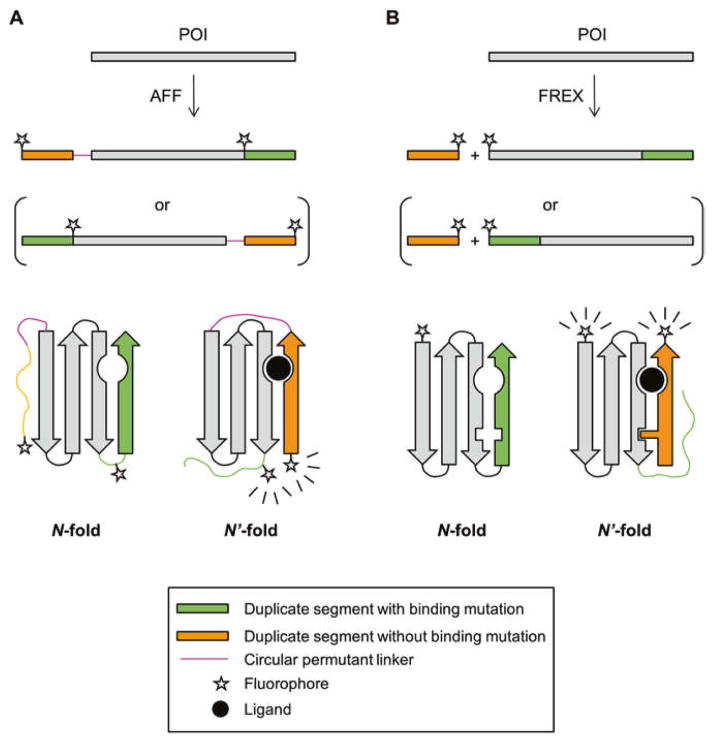
Fig. 1.
Schematic of AFF (a) and FREX (b) switching mechanisms. Primary amino acid sequences are indicated by horizontal bars with folded protein structures represented below the sequences. For the two sequences in parentheses an N-terminal segment (containing a critical binding residue) is duplicated. The other two sequences, and the structures that result from their folding, represent the analogous case in which a C-terminal segment is duplicated. Wavy lines indicate the copy of the duplicate segment that is orphaned in N and N′ conformations and is hence unfolded. The N-fold of POI-FREX is shown with a packing mutation in the green arrow that is swapped out by the wild-type residue from the orange arrow in the N′-fold