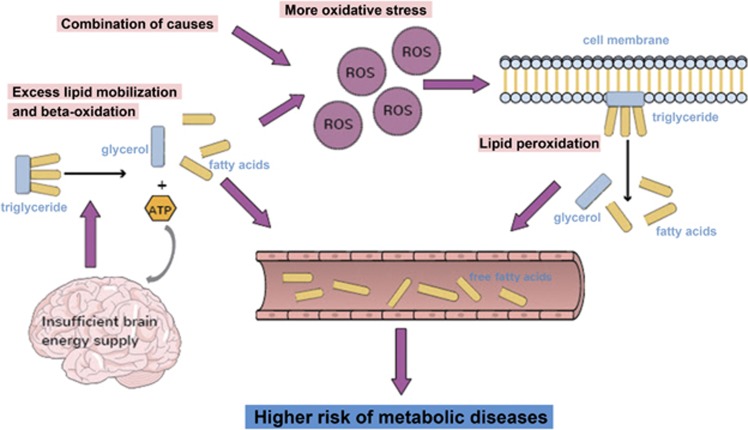
Figure 3.
The systemic alterations resulting in the changes in free fatty acids (FFA) patterns in schizophrenia patients. Insufficient energy supply in the brains of schizophrenia patients causes excess lipolysis and β-oxidation, accompanied by FFA and ROS accumulation. Additional oxidative stress caused by active β-oxidation and other factors results in lipid peroxidation, causing loss of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) from the lipid membrane. The increased FFAs increase the risk of metabolic diseases such as cardiovascular diseases and type II diabetes in schizophrenia patients.