Figure 6. Disruption of sialic acids increases microvascular permeability to water and albumin.
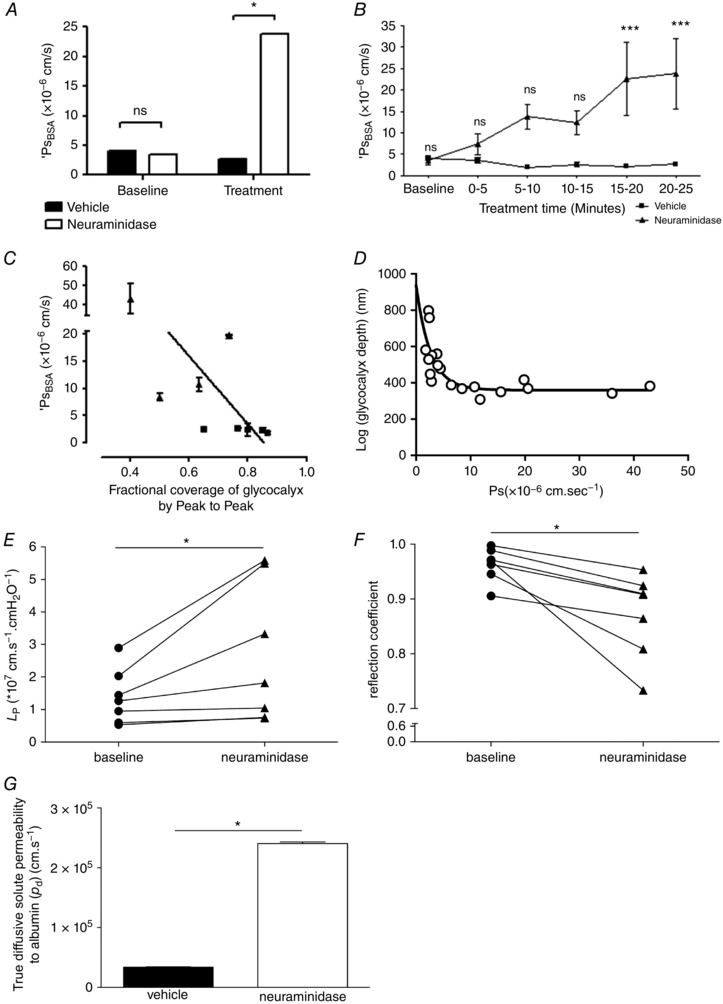
A, apparent solute permeability to albumin (P sBSA) was measured in microvessels before (baseline) and 20–25 min after (treatment) perfusion with either vehicle (filled bars) or neuraminidase (open bars). Sialic acid disruption with neuraminidase perfusion significantly increased P sBSA (* P < 0.05, two‐way ANOVA post hoc Bonferroni analysis), with no significant change in P sBSA in vehicle‐perfused control vessels (ns, P > 0.05, two‐way ANOVA post hoc Bonferroni analysis). B, P sBSA increased progressively over time during neuraminidase perfusion (filled triangles), but remained unaltered during vehicle perfusion (filled squares). A significant increase in P sBSA was noted after 15–20 min treatment with neuraminidase, matching the time course of neuraminidase‐induced endothelial glycocalyx disruption (*** P < 0.001, two‐way ANOVA, Bonferroni post hoc analysis). A significant inverse correlation was noted between P sBSA and fractional coverage by resolvable endothelial glycocalyx determined with the peak to peak method (C) (r = −0.73, P < 0.05 Pearson correlation). A significant relation between P sBSA and endothelial glycocalyx depth determined with the peak to peak method was best described by a single one‐phase decay curve with a relationship of depth = 330 nm + 607 nm × e−0.38× P s (D). Microvessel hydraulic conductivity (L P) was significantly increased after sialic acid disruption with 20–25 min perfusion with neuraminidase (filled triangles) compared with baseline measurements in the same vessel (filled circles) (* P < 0.05, Wilcoxon) (E). Microvessel reflection coefficient to albumin was significantly reduced after sialic acid disruption with 20–25 min perfusion with neuraminidase (filled triangles) compared with baseline measurements in the same vessel (filled circles) (* P < 0.05, Wilcoxon) (F). There was a significant increase in true diffusive solute permeability to albumin after sialic acid disruption with neuraminidase (* P < 0.001, unpaired t test) (G).
