Figure 2. Current conceptual model of outcomes of sepsis.
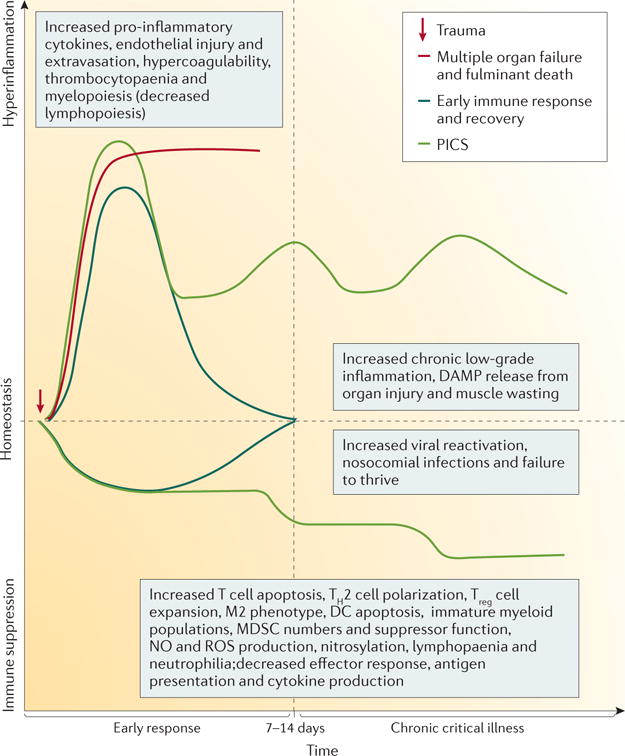
Originally conceived by Bone et al.165 in the 1990s, the current model of the clinical trajectory that patients traverse in sepsis has evolved to reflect the concurrent inflammatory and immunosuppressive responses, and the observation that fewer patients are dying in the early period owing to earlier recognition and better implementation of best clinical practices50. Successful resuscitation is occurring more frequently and the patients recover sufficiently to be discharged from the intensive care unit and hospital (blue lines). Some patients experience a pronounced early inflammatory response to the pathogen or danger signals, leading to multiple organ failure and death (red line). Other patients survive the early inflammatory response but experience chronic critical illness (green lines) that is characterized by persistent inflammation, immunosuppression and catabolism syndrome (PICS); reactivation of latent viral infections; nosocomial infections; and long-term functional and cognitive declines52. DAMP, damage-associated molecular pattern; DC, dendritic cell; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cell; NO, nitric oxide; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TH2, T helper 2.
