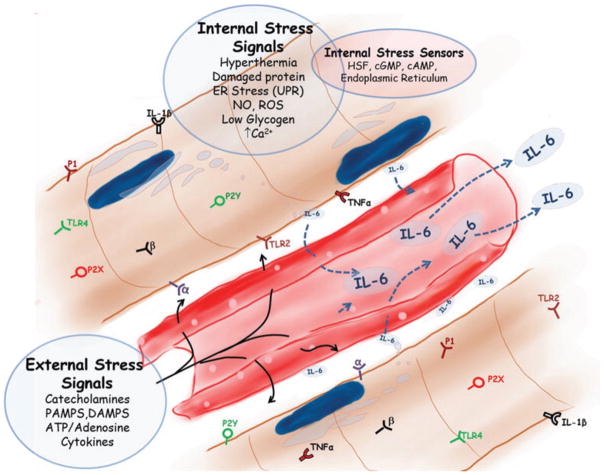
Figure 1. The internal and external stress-related signals that skeletal muscle is equipped to detect via receptors or second messengers and that are genomically linked to regulation of the interleukin-6 (IL-6) gene.
Abbreviations: P2X, Purinergic receptor type 2 X; P2Y, Purinergic receptor type 2 Y; P1, Purinergic receptor type 1; IL-6, Interleukin-6; TNF-alpha, Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha; IL-1Beta, Interleukin-1Beta; UPR, Unfolded Protein Response; ER, Endoplasmic Reticulum; NO, Nitric Oxide; ROS, Reactive Oxygen Species; Ca2+, Calcium; TLR 2, Toll-Like Receptor 2; TLR 4, Toll-Like Receptor 4; beta, Beta-adrenergic receptor; alpha, Alpha-adrenergic receptor; HSF, Heat Shock Factor; cGMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; PAMPS, Pathogen associated molecular patterns; DAMPs, Damage associated molecular patterns; ATP, Adenosine Triphosphate.