Figure 2.
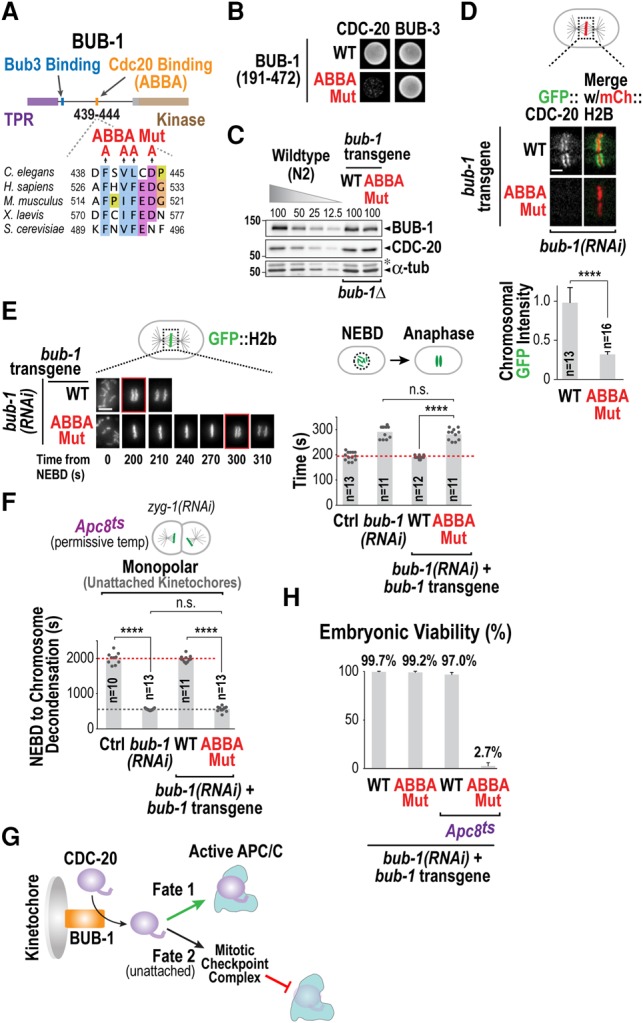
The ABBA motif of BUB-1 recruits CDC-20 to both promote APC/C activation and generate a checkpoint signal at unattached kinetochores. (A) Schematic of BUB-1 and its conserved ABBA motif. Alanine mutations introduced in the ABBA motif are indicated. (B) Yeast two-hybrid analysis of a BUB-1 fragment that interacts with both CDC-20 and BUB-3. (C) Immunoblots of transgene-encoded BUB-1 (wild-type [WT] or ABBA mutant [Mut]) and endogenous CDC-20 in the absence of endogenous BUB-1. A dilution curve of wild-type (N2) worms is on the same blot for comparison. α-Tubulin served as a loading control. The asterisk denotes residual CDC-20 signal after reblotting. (D) Metaphase images (top) and quantification (bottom) of GFP::CDC-20 chromosomal fluorescence for the indicated conditions. Error bars are the 95% confidence interval. (****) P < 0.0001 (Mann-Whitney test). Bar, 2 µm. (E) Images from time-lapse sequences (left) and quantification of the NEBD–anaphase onset interval (right) of embryos expressing GFP::H2b for the indicated conditions. Time below panels is seconds relative to NEBD. (****) P < 0.0001 (Mann-Whitney test). Bar, 5 µm. (F) Quantification of checkpoint signaling in two-cell embryos in the presence of unattached kinetochores for the indicated conditions. Mitotic duration is the NEBD–chromosome decondensation interval. (****) P < 0.0001 (Mann-Whitney test). (G) Schematic summarizing two opposing fates of CDC-20 that is fluxing through kinetochores via interaction with the ABBA motif of BUB-1. (H) Embryo viability analysis for the indicated conditions. At least 14 worms and 2330 embryos were scored per condition. Error bars represent the standard deviation. See also Supplemental Figure S2.
