Abstract
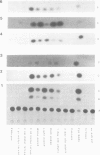
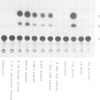
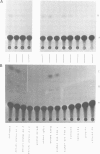
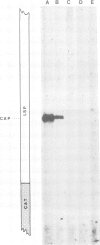
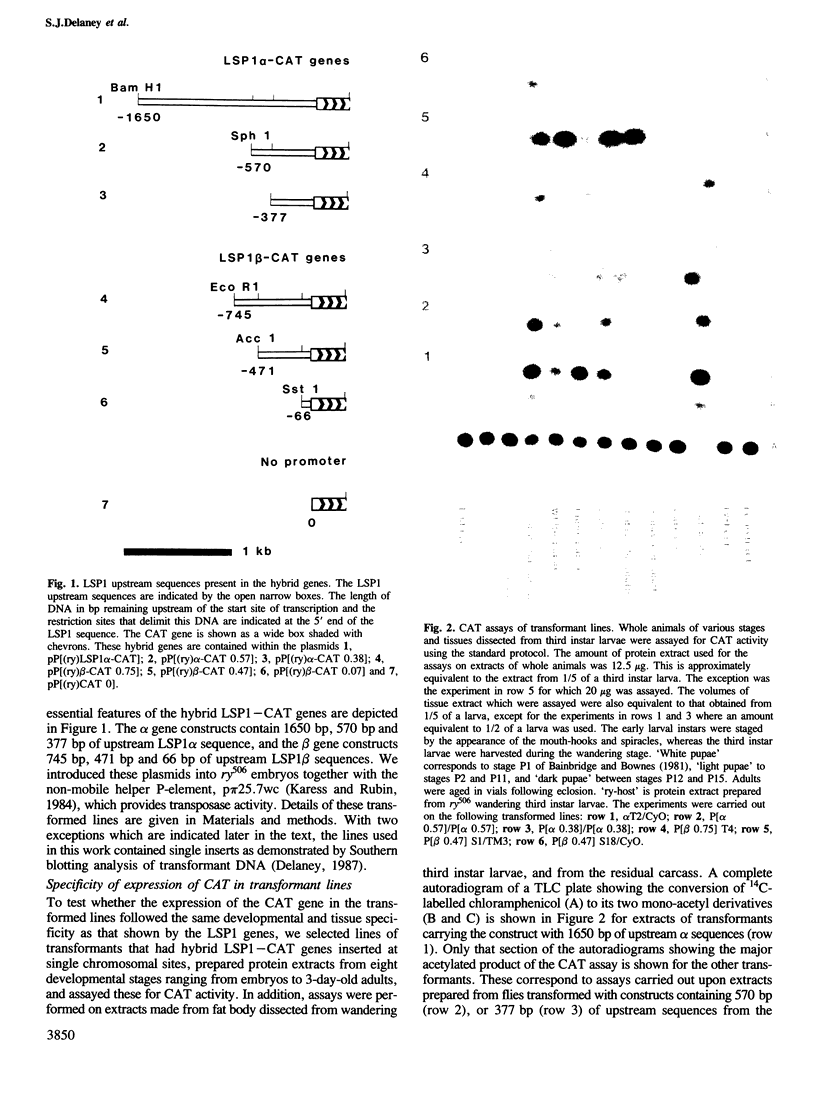
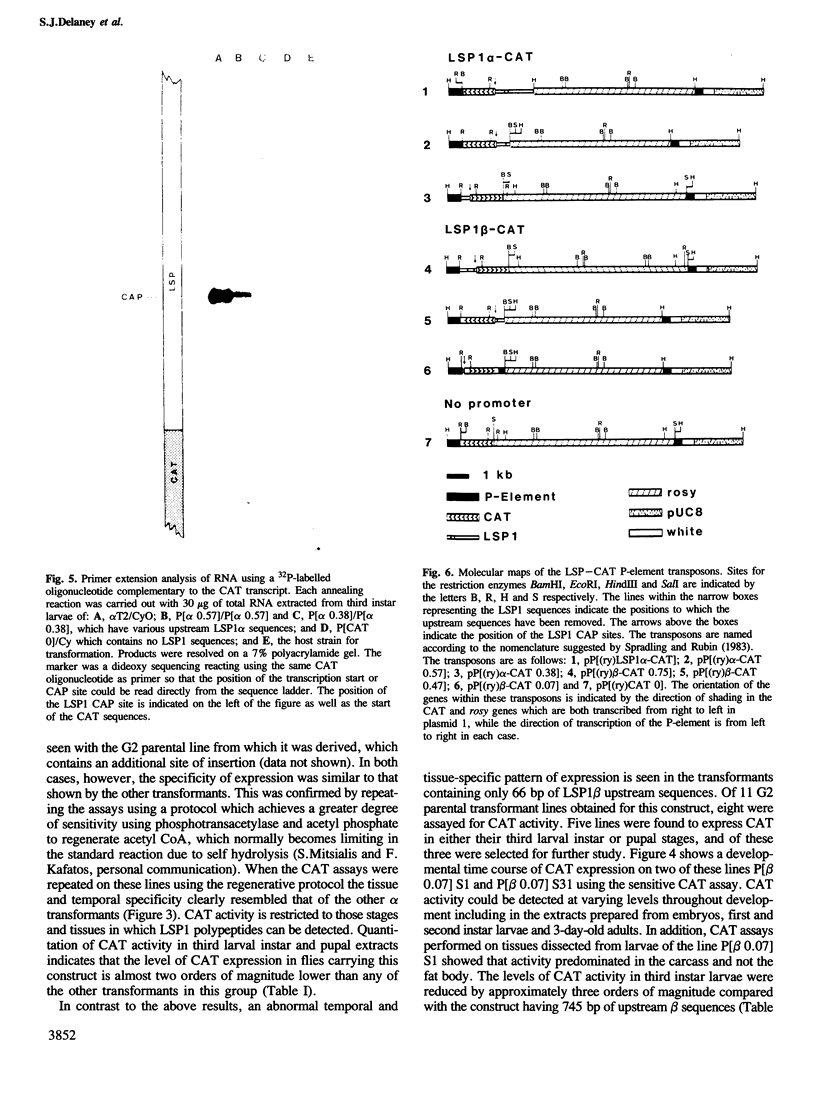
We have constructed hybrid genes in which the coding region of the bacterial gene chloramphenicol acetyl transferase (CAT) has been linked to varying lengths of upstream sequences of Drosophila genes for larval serum sequence 1 (LSP1). These have been inserted into a P-element transformation vector and subsequently transferred into the germ-line of recipient flies. Transformants carrying the CAT gene linked to 1650 bp, 570 bp or 377 bp of upstream LSP1α sequences, or 745 bp or 471 bp of upstream β sequences express CAT with the same developmental and tissue specificity as the endogenous LSP1 genes. Constructs having only 66 bp of upstream LSP1β sequences, however, show extremely low levels of CAT expression in tissues and at developmental stages in which LSP1 is not expressed. We discuss the significance of short regions of homology between the DNA upstream of the α and β genes, which lie within the regions identified by the transformation experiments as being required for the cis-regulation of LSP1 synthesis.
Keywords: Drosophila, LSP1 genes, transformation, CAT, developmental specificity
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bainbridge S. P., Bownes M. Staging the metamorphosis of Drosophila melanogaster. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1981 Dec;66:57–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock H. W., Roberts D. B. Comparison of the larval serum proteins of Drosophila melanogaster using one and two-dimensional peptide mapping. Eur J Biochem. 1980 May;106(1):129–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covington M., Fleenor D., Devlin R. B. Analysis of xanthine dehydrogenase mRNA levels in mutants affecting the expression of the rosy locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4559–4573. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. A., Addison C. F., Delaney S. J., Sunkel C., Glover D. M. Expression of the prokaryotic gene for chloramphenicol acetyl transferase in Drosophila under the control of larval serum protein 1 gene promoters. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):13–24. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90377-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaney S. J., Smith D. F., McClelland A., Sunkel C., Glover D. M. Sequence conservation around the 5' ends of the larval serum protein 1 genes of Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90376-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jowett T. The regulatory domain of a larval serum protein gene in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3789–3795. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04149.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karess R. E., Rubin G. M. Analysis of P transposable element functions in Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):135–146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90534-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland A., Smith D. F., Glover D. M. Short intervening sequences close to the 5' ends of the three Drosophila larval serum protein 1 genes. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 5;153(2):257–272. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90277-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D. B., Evans-Roberts S. The genetic and cytogenetic localization of the three structural genes coding for the major protein of drosophila larval serum. Genetics. 1979 Nov;93(3):663–679. doi: 10.1093/genetics/93.3.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Vectors for P element-mediated gene transfer in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6341–6351. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. F., McClelland A., White B. N., Addison C. F., Glover D. M. The molecular cloning of a dispersed set of developmentally regulated genes which encode the major larval serum protein of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):441–449. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Rubin G. M. The effect of chromosomal position on the expression of the Drosophila xanthine dehydrogenase gene. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):47–57. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90135-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Rubin G. M. Transposition of cloned P elements into Drosophila germ line chromosomes. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):341–347. doi: 10.1126/science.6289435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. D., Edlund T., Boulet A. M., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression controlled by the 5'-flanking region of insulin and chymotrypsin genes. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):557–561. doi: 10.1038/306557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe J., Akam M. E., Roberts D. B. Biochemical and immunological studies on larval serum protein 1, the major haemolymph protein of Drosophila melanogaster third-instar larvae. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Sep 15;79(1):47–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11782.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]