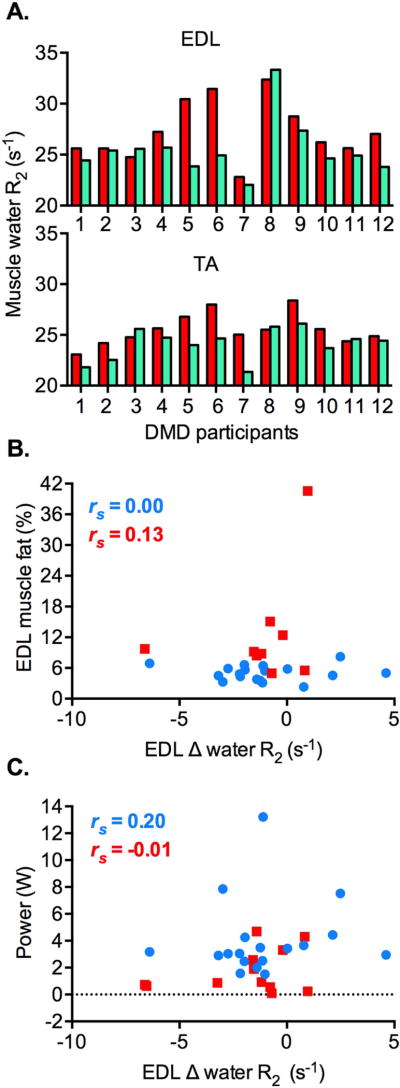
Figure 3.
Changes in muscle water R2 (s−1) in the ankle dorsiflexor muscles of DMD participants and the healthy volunteers following the volitional ankle dorsiflexion exercise. A. Congruent changes in muscle water R2 between baseline (red) and 3 hours post-exercise (green) in the tibialis anterior (TA) and extensor digitorum longus (EDL) muscles of individual DMD participants (n = 12). A decrease in muscle water R2 is seen in 10 DMD patients, whereas an increase in water R2 is seen in 2 patients. B. There is no significant correlation between Δ muscle water R2 and muscle fat (%) in the EDL muscle of DMD patients (red squares; n = 9, p = 0.743) and the healthy volunteers (blue circles; n = 18, p = 0.990). C. Similarly, Δ water R2 of the EDL muscle is not significantly correlated with power exerted over the course of the exercise in the DMD participants (red squares; n = 12, p = 0.991) and healthy volunteers (blue circles; n = 18, p = 0.433). Spearman’s r (rs) is shown.