Figure EV5. Analysis of Xenopus pwwp2a expression and function.
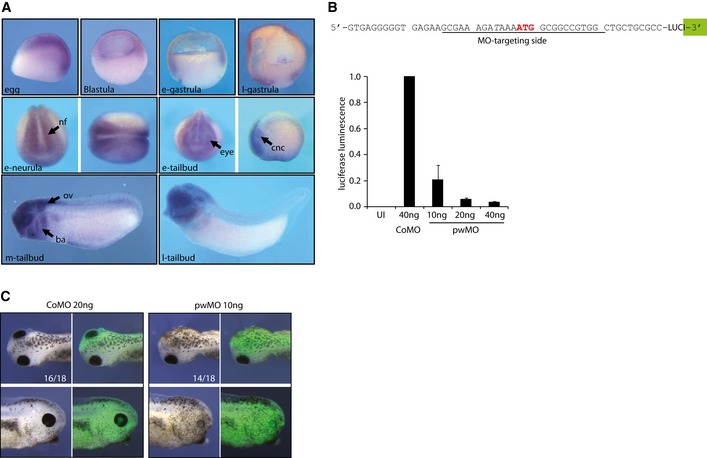
- Expression pattern of endogenous Xenopus tropicalis pwwp2a mRNA during early development. Pictures show whole‐mount RNA in situ hybridization patterns (purple color) for the following developmental stages: egg, blastula and early (e‐)/late (l‐) gastrula stages in lateral views of sagittal sections; e‐neurula and e‐tailbud stages show anterior views (left picture) or dorsal views (right picture, anterior to the left). Mid (m‐) and l‐tailbud stages are shown in lateral views (anterior left). Abbreviations: ba, branchial arches; cnc, cranial neural crest; eye, retinal Anlage; nf, neural folds; ov, otic vesicle.
- Top: Targeting region of the pwMO oligonucleotide on the X. laevis pwwp2a mRNA. The translational start site is highlighted in red. To determine the translational blocking efficiency of pwMO in vivo, a ˜275‐bp fragment of pwwp2a 5′ cDNA sequence, including the AUG, was cloned in frame upstream of the luciferase coding region. Bottom: The above depicted luciferase construct was injected in CoMO‐ or pwMO‐loaded embryos and chemiluminescence measured at gastrula stage. Error bars indicate SEM of three independent biological replicates. UI, uninjected embryos.
- Morphology of X. tropicalis embryos injected with CoMO and pwMO together with lineage‐tracer Alexa‐488; numbers indicate penetrance of major morphological phenotype over total embryos inspected (n = 3 experiments).
