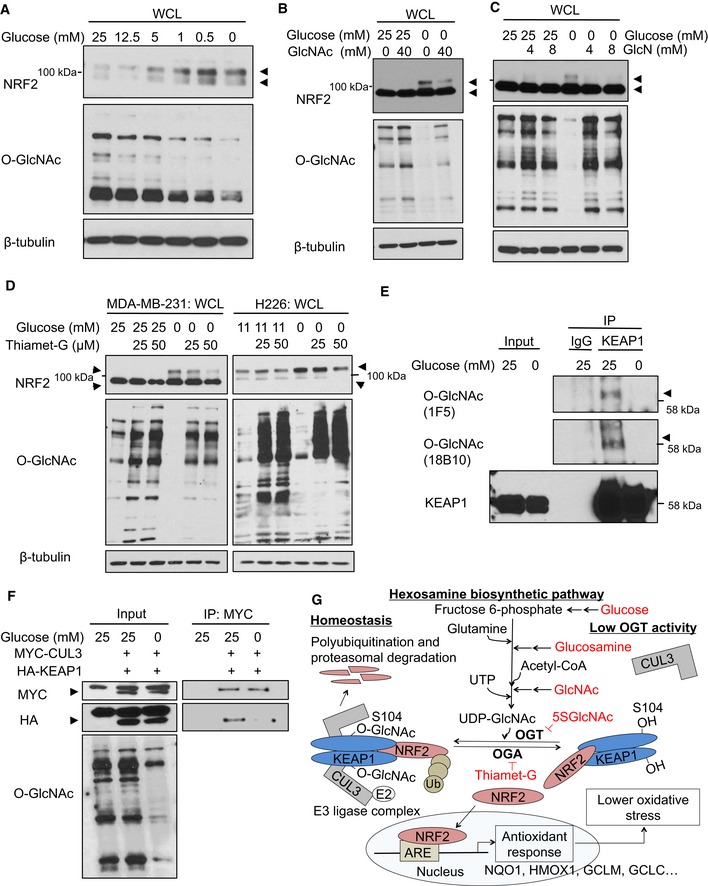
Figure 6. KEAP1 O‐GlcNAcylation and NRF2 stability are regulated by glucose levels.
-
ANRF2 protein levels anti‐correlate with both glucose levels and global O‐GlcNAcylation. MCF7 cells were incubated with the indicated glucose concentrations for 12 h, and WCLs were analyzed by Western blot. Arrows indicate NRF2.
-
B, CGlcNAc (B) or GlcN (C) supplementation suppresses NRF2 induction by glucose deprivation. MDA‐MB‐231 cells were incubated with the indicated levels of glucose and GlcNAc (B) or GlcN (C) for 16 h, and WCLs were analyzed by Western blot. Arrows indicate NRF2.
-
DBlocking OGA activity abolishes NRF2 induction by glucose deprivation. MDA‐MB‐231 or H226 cells were treated with Thiamet‐G for 8 or 24 h, respectively, and then subjected to glucose deprivation for additional 16 or 24 h, respectively. WCLs were analyzed by Western blot. Arrows indicate NRF2.
-
EGlucose deprivation reduces KEAP1 O‐GlcNAcylation. MDA‐MB‐231 cells were incubated with 25 or 0 mM glucose for 16 h and lysates were analyzed by IP/Western blot. Arrow indicates O‐GlcNAcylated KEAP1.
-
FGlucose deprivation reduces the KEAP1–CUL3 interaction. MDA‐MB‐231 cells were transfected with HA‐KEAP1 and MYC‐CUL3 for 24 h and then subjected to the indicated glucose concentrations for additional 12 h. Lysates were analyzed by IP/Western blot. Arrow indicates overexpressed MYC‐CUL3 or HA‐KEAP1, respectively.
-
GProposed model, in which nutrient‐sensitive KEAP1 S104 O‐GlcNAcylation promotes its productive interaction with CUL3 to mediate NRF2 ubiquitination and destruction. Please see text for details.
Source data are available online for this figure.
