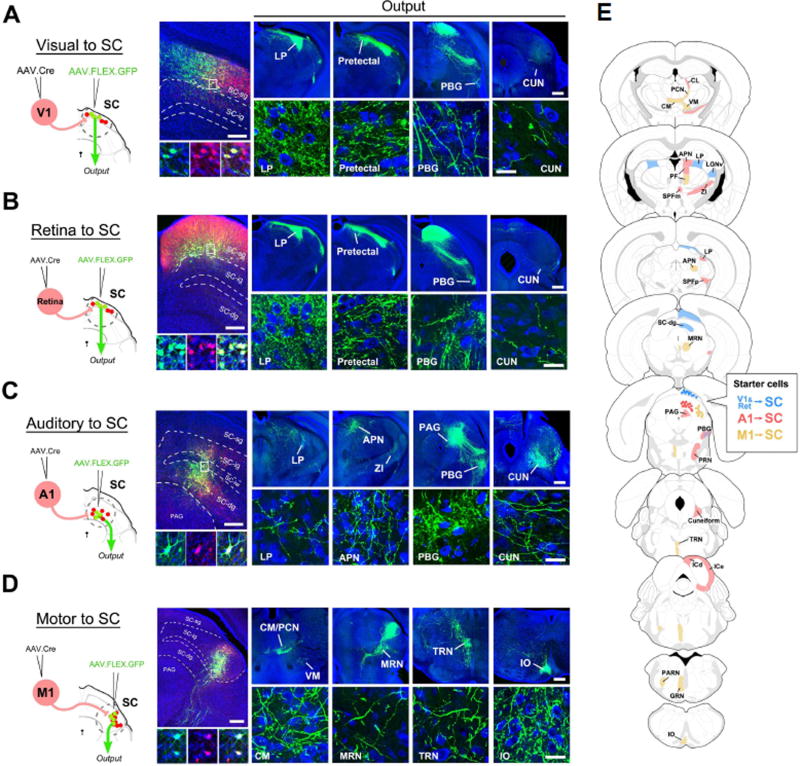
Figure 5. Mapping of axonal outputs of input-defined neuronal populations in SC.
(A) Left, AAV1-hSyn-Cre was injected into V1 of Ai14 mice, followed by a second injection of AAV1-CAG-FLEX-GFP into SC. Middle, GFP-labeled neurons in SC-sg were also tdTomato+. Right four panels, GFP-labeled axons in various regions (LP, pretectal area, PBG, cuneiform nucleus (CUN)) downstream of SC. High-magnification images (bottom) reveal ramified axons and their terminal and bouton structures. Blue, Nissl staining. Scale bars: 250 µm, middle top panel; 500 µm, right top panels; 25 µm, bottom panels. The scales also apply to (B), (C), (D) correspondingly.
(B) Axonal outputs of SC-sg neurons that receive input from the contralateral retina. Data are displayed in a similar way as in (A).
(C) Axonal outputs of SC neurons that receive input from A1, which are located mainly in SC-dg and sparsely in SC-ig.
(D) Axonal outputs of SC neurons that receive input from M1, which are located mainly in the lateral aspect of SC-ig.
(E) Summary of observed target regions for SC neuron subpopulations receiving input from V1/retina (blue), from A1 (red), and from M1 (yellow) respectively. Abbreviations: CL, central lateral nucleus of thalamus; PCN, paracentral nucleus; VM, ventral medial nucleus of thalamus; CM, central medial nucleus of thalamus; APN, anterior pretectal nucleus; PF, parafascicular nucleus; SPFm and SPFp, subparafascicular nucleus, magnocellular and parvicellular; ZI, zona incerta; MRN, midbrain reticular nucleus; PRN, pontine reticular nucleus; TRN, tegmental reticular nucleus; ICd and ICe, inferior colliculus, dorsal and external; PARN, parvicellular reticular nucleus; GRN, gigantocellular reticular nucleus; IO inferior olivary complex.