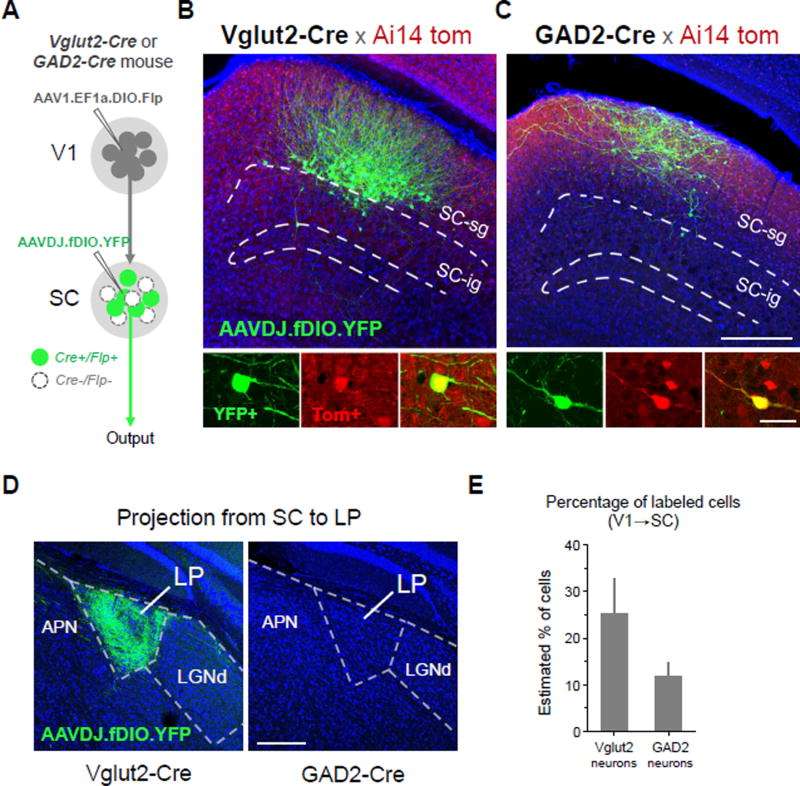
Figure 8. Cell-type specific anterograde transneuronal labeling.
(A) Strategy for labeling glutamatergic (Vglut2-Cre+) or GABAergic (GAD2-Cre+) subpopulations of SC neurons that receive input from V1.
(B) Selective labeling of V1-recipient glutamatergic neurons in superficial layers of SC. Anterograde transneuronal transport of AAV1-EF1a-DIO-Flp enables Cre-dependent expression of Flp in glutamateric neurons (Ai14 tdTomato+) receiving input from V1. A second injection of AAVDJ-fDIO-YFP into SC enables Flp-dependent expression of YFP specifically in V1-recipient glutamatergic neurons (green), filling soma, dendrites, and axons. YFP+ neurons co-localize with Ai14 tdTomato expression in Vglut2-Cre+ neurons (bottom panels, enhanced with anti-RFP immunostaining).
(C) Selective labeling of V1-recipient GABAergic neurons using same strategy as in (B) but with injections in a GAD2-Cre mouse. Scale: 250 µm, top panel; 25 µm bottom panel. The scales also apply to (B) correspondingly.
(D) Long range axonal projection to LP from glutamatergic, but not GABAergic, V1-recipient SC neurons. Scale: 250 µm.
(E) Percentage of YFP+/Tomato+ cells out of total Tomato+ cells quantified for local regions expressing YFP in Vglut2-Cre and GAD2-Cre mice (4 week post-injection survival, 60 nl injections, n = 4 each). Error bar = SD.