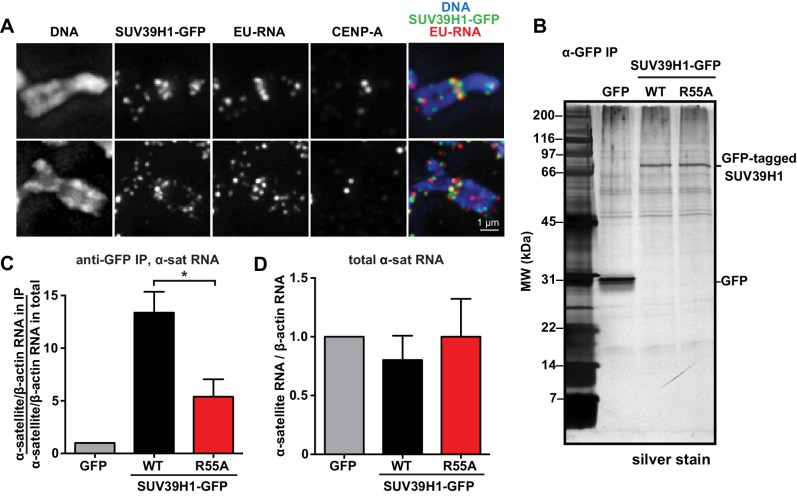
Figure 5. SUV39H1 association with α-satellite RNA in vivo depends on direct nucleic acid binding.
(A) Colocalization of SUV39H1 and RNA at pericentric regions. SUV39H1-GFP expressing HeLa cells were labeled with EU and induced with doxycycline for 6 hr, then mitotic cells were spun onto coverslips. Cells were stained for DNA (blue), with anti-GFP to detect SUV39H1-GFP (green), for EU-RNA (red), and CENP-A to mark centromeres. (B) Silver stained gel showing protein immunoprecipitated by an anti-GFP antibody from cell lines expressing GFP, SUV39H1-GFP, or SUV39H1R55A-GFP. (C) Quantification of α-satellite RNA immunoprecipitated with SUV39H1. RNA was isolated from IPs, and RT-qPCR was performed to detect α-satellite RNA sequence. Enrichment values are the ratio of α-satellite/β-actin RNA in the IP over the ratio of α-satellite/β-actin RNA in total lysate, normalized to the GFP values. Error bars are standard error, n = 3, *p<0.04. (D) Total α-satellite RNA levels in GFP, SUV39H1-GFP, and SUV39H1R55A-GFP cell lines, divided by the amount of β-actin RNA, normalized to the GFP values. See also Figure 5—figure supplement 1.
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. Immunoprecipitation of SUV39H1-GFP from human cells.