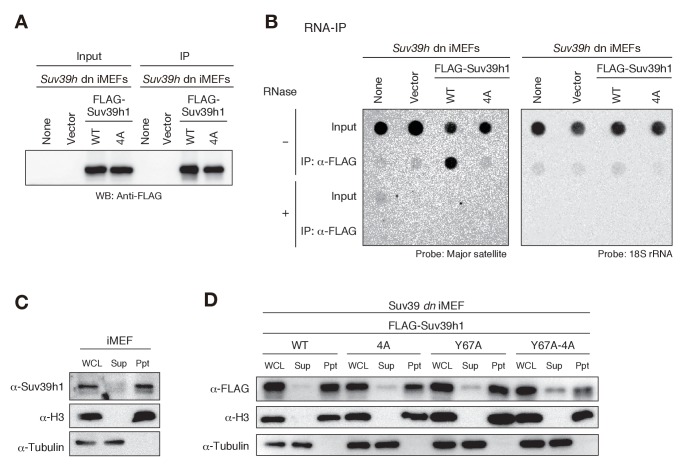
Figure 4. Suv39h1-CD’s nucleic acid binding is required for its interaction with major satellite RNAs in vivo.
(A) Whole cell lysates (input) of Suv39h dn iMEFs expressing FLAG-tagged wild-type (WT) or mutant (4A) Suv39h1 and FLAG immunoprecipitates (IP) were subjected to immunoblotting using an anti-FLAG M2 antibody. Parental Suv39h dn iMEFs (none) and Suv39h dn iMEFs with an empty vector (vector) were used as controls. (B) Dot-blot analysis of immunoprecipitated RNAs. RNAs associated with WT or mutant (4A) Suv39h1 in Suv39h dn iMEFs were precipitated with the anti-FLAG M2 antibody and subjected to dot-blot analysis using a labeled probe for major satellite repeats (left) and 18S rRNA (right). (C, D) Chromatin fractionation assays were performed using control iMEFs (C) and Suv39h dn iMEFs expressing FLAG-tagged WT or mutant Suv39h1 (D). Soluble (Sup) and insoluble chromatin-enriched (Ppt) fractions were resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting. For comparison, anti-α-tubulin and anti-histone H3 antibodies were used to detect soluble- and chromatin-associated proteins, respectively.
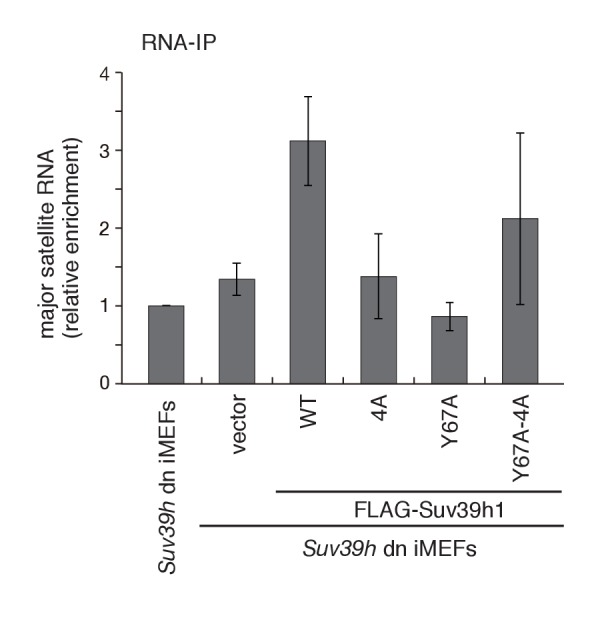
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Both Suv39h1-CD’s nucleic acid- and H3K9me3 binding activities are required for its interaction with major satellite RNAs in vivo.