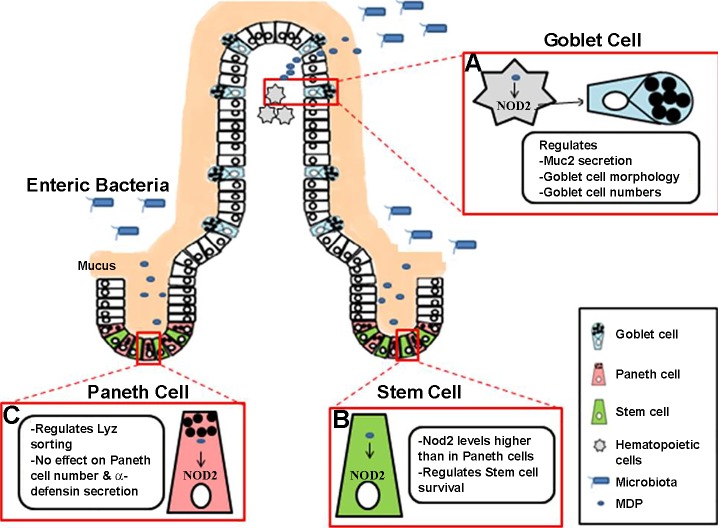
Fig. 1.
NOD2-mediated bacterial sensing and modulation of intestinal epithelial homeostasis. Binding of bacterial MDP to cytosolic NOD2 receptors appears to have comprehensive influences on intestinal mucosal homeostasis. A: incursion of pathogenic microorganisms or detrimental expansion of commensal bacteria may be sensed by hematopoietic NOD2-expressing cells that regulate goblet cell number and morphology, as well as the expression and secretion of antimicrobial gene products such as mucin 2. B: crypt base columnar (CBC) stem cells express higher levels of NOD2 compared with the Paneth cells. MDP sensing by NOD2 appears to influence stem cell renewal or/and survival. C: NOD2, as well as NOD2-mediated bacterial sensing, may regulate lysozyme sorting in Paneth cells, although the expression of several antimicrobial peptides, such as α-defensin, is not dependent on NOD2.