Fig. 5.
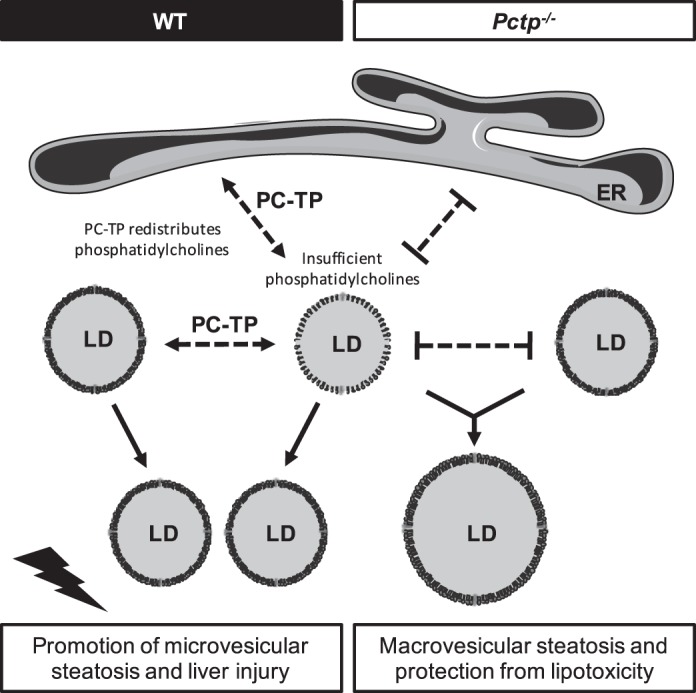
Schematic diagram: MCD diet reduces hepatic phosphatidylcholine concentrations. Under these limiting conditions, PC-TP is upregulated and functions to redistribute phosphatidylcholine molecules between the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and lipid droplets (LDs) with sufficient or excess phosphatidylcholine, to preserve the stability of small LDs that promote liver injury. In the absence of PC-TP, smaller lipid droplets with insufficient phosphatidylcholine on their surfaces coalesce into larger lipid droplets that are less metabolically active and hepatotoxic.
